How To: Rasterization and Vectorization Conversion
Rasterization converts vectors into rasters. While vectorization transforms rasters in vectors. We explain how to go from one data model to the other.

Rasterization converts vectors into rasters. While vectorization transforms rasters in vectors. We explain how to go from one data model to the other.

The least cost path finds the most cost-effective path, from a start point to a destination, making it a useful tool for linear routing.
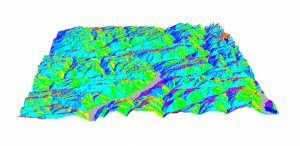
In the mountains, the terrain slopes are in all directions – east, west, north and south-facing. The compass direction that the slope faces is slope aspect.
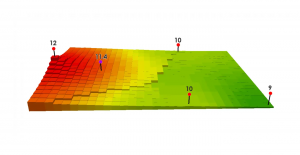
Inverse Distance Weighting (IDW) interpolation estimates unknown values with specifying search distance, closest points, power setting & barriers.
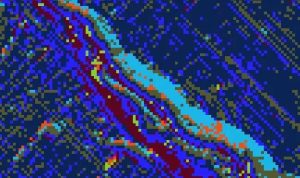
Flow direction calculates the direction water will flow in its eight adjacent cells using slope from neighboring cells (in a raster grid cell)
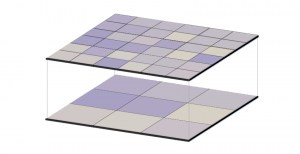
For raster resampling in GIS, you can use bilinear and cubic convolution for continuous data as well as nearest neighbor and majority for discrete data.

SAGA GIS has a quick and dirty tool to fill NoData holes with raster data. We show you how to close gaps in DEMs or any raster data with holes in it.
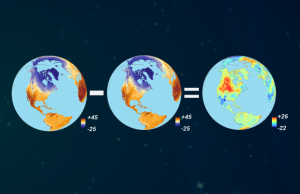
Map algebra is a cell-by-cell combination of stacked raster grids. It uses math-like functions with arithmetic, statistics and trigonometry operators.

Learn how to clip rasters in ArGIS using the raster clip tool in ArcToolbox as well as the clip button as part of the Raster Functions.