What is Conflation, Edge Matching and Rubbersheeting?
When you have two conflicting data sets, conflation resolves conflicts by preserving the most accurate one. Edgematching and rubbersheeting helps fix errors
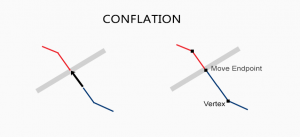
When you have two conflicting data sets, conflation resolves conflicts by preserving the most accurate one. Edgematching and rubbersheeting helps fix errors
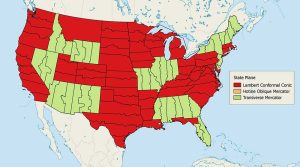
The State Plane Coordinate System divides the United States into 124 zones to locate any point with a high level of accuracy (one part in 10,000).
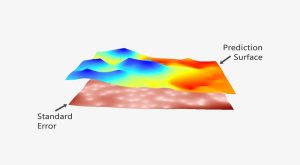
The prediction is strong in kriging. In this guide to geostatistics we embark on a journey to sculpt a legendary prediction model with kriging interpolation
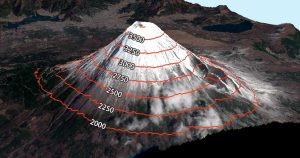
Contour lines have constant values on them such as elevation. But it’s also used in meteorology (isopleth), magnetism (isogon) & even drive-time (isochrones)
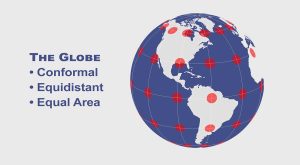
Map distortion is best understood looking at Tissot’s indicatrix. It contains circles and shows how map projections distort shape, size and distances.

Have you ever wanted to create interactive web maps for your organization? Or how about the whole world? You can with Esri’s cloud-based ArcGIS Online.

While geosynchronous satellites can have any inclination, the key difference is that satellites in geostationary orbit lie on the same plane as the equator.

Some things in life are certain. In ArcGIS, it’s the Esri 999999 error. Here are techniques to troubleshoot this ArcMap error.
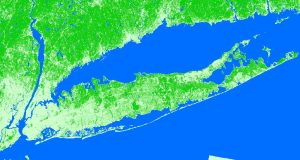
Over the span of your life, how much has the Earth changed? Quite a bit, but you probably just can’t put a number to it. You actually CAN with land cover.
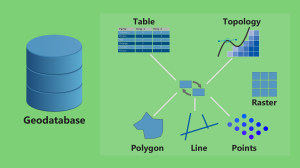
If you’re a bit confused whether or not to use a file geodatabase (*.gdb) or a personal geodatabase (*.mdb)… Here’s everything you need to know.