Light Reflection, Absorption and Transmission in Remote Sensing
The EM radiation that makes it to Earth is called incident light. From here, Earth’s features reflect, absorb and transmit different amounts of energy.
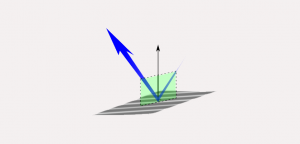
The EM radiation that makes it to Earth is called incident light. From here, Earth’s features reflect, absorb and transmit different amounts of energy.
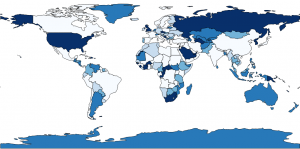
Equal intervals, quantile, natural breaks, pretty breaks- data classification methods generate different choropleth maps. We explain the types of maps here.
Companies, government, and the military embrace GeoMedia because of its solution-driven approach and its ability to extract actionable information.

From passive to active remote sensing – photogrammetry to LiDAR, ERDAS Imagine loads you with all the necessary tools for more robust image analysis.
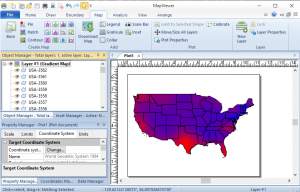
Golden Software MapViewer emphasizes scientific data mapping, modeling, and analysis. But it can also work with various thematic maps.

Today’s farmers use sophisticated agriculture technology because they can save time and money. Location-based GIS helps farmers solve the answer ‘where’.

GRASS GIS (Geographic Resources Analysis Support System) is one of the oldest public domain GIS software in existence – over 30 years old.
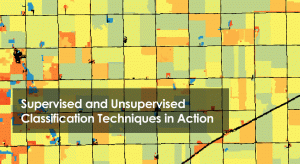
Supervised classification creates training areas, signature file and classifies. Unsupervised classification generate clusters and assigns classes.

Businesses around the world are embracing commercial GIS software because sometimes it just makes more business sense. We list commercial mapping software.

The least cost path finds the most cost-effective path, from a start point to a destination, making it a useful tool for linear routing.