GEOINT – Geospatial Intelligence

GEOINT stands for Geospatial Intelligence. It’s about gathering data from maps and satellite images. This helps in understanding physical features and human activities for governments and businesses.
GEOINT includes collecting and analyzing visual information through the use of satellites. For example, an analyst may keep an eye on military movements or plan for disaster management.
Careers in Geospatial Intelligence
To get a better understanding of GEOINT, I think it would be helpful to understand some of the available careers. Here are some paths you could explore:
- Imagery Analyst: They interpret satellite and aerial imagery to understand ground conditions.
- GIS Specialist: Focuses on creating and managing geographic data using GIS software.
- Geospatial Engineer: Works on developing the tools and systems used to collect and analyze geospatial data.
- Remote Sensing Scientist: Specializes in analyzing data collected from remote sensors, like satellites.
- Intelligence Analyst: Uses geospatial data to support military or national security missions.
- Cartographer: Designs and updates maps using geospatial information.
- GEOINT Data Analyst: Analyzes GIS datasets to uncover patterns or trends related to geospatial intelligence.
In these careers, users blend technology, geography, and analytical skills. So, a career in GEOINT can lead to many interesting opportunities. From protecting the environment to national security, the rise of technology means it’s always evolving.
NGA GEOINT
The NGA, or National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency, plays a key role in GEOINT. It’s a U.S. government agency tasked with collecting and analyzing geospatial intelligence.

The NGA supports national security by providing GEOINT to U.S. defense and intelligence communities. Their work includes mapping, imagery, and satellite data analysis.
NGA GEOINT helps plan military operations and ensure troop safety. In fact, the NGA contributed to the mission that located Osama bin Laden. Aside from military usage, the NGA also aids in disaster relief by mapping affected areas for rescue efforts.
USGIF GEOINT
The USGIF, or United States Geospatial Intelligence Foundation, is unique in the GEOINT world. It’s not a government agency, but a nonprofit organization. Its main goal is to promote the geospatial intelligence tradecraft.
The USGIF brings together professionals from government, industry, and academia. This collaboration helps in advancing GEOINT for national security and beyond. For example, they offer education, training, and resources to GEOINT professionals.
The USGIF also hosts the annual GEOINT Symposium, a key event for networking and innovation. By bringing together this community, the USGIF supports the development of new methodologies. So, the USGIF plays a crucial role in shaping the future of GEOINT.
GEOINT Examples and Use Cases
GEOINT plays a key role in society in many ways. Here are some examples:
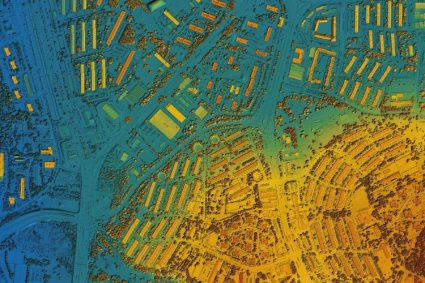
- Disaster Response: After a natural disaster, GEOINT helps assess damage and plan rescues.
- Climate Change: It tracks changes in the environment, like deforestation or melting ice.
- Urban Planning: Cities use GEOINT to plan roads, parks, and buildings.
- Agriculture: Farmers use satellite images to monitor crops and improve yields.
- Military Operations: Armies use GEOINT to understand terrain and plan missions.
- Navigation: GEOINT data powers GPS systems in cars and phones.
- Border Security: It helps monitor and secure national borders.
- Maritime Safety: Ships use GEOINT for safe navigation and to avoid hazards.
- Public Health: Tracking the spread of diseases can be aided by GEOINT.
So, GEOINT is everywhere. It helps many fields because it provides a larger picture from above.
Data & Analysis in Geospatial Intelligence
Satellites capture imagery from space, which experts then analyze. Satellite imagery is key for intelligence analysis. While satellites are key in data collection, drones, and aerial photography are also important.
Because GEOINT gives a bird’s-eye view, it’s through Imagery Intelligence (IMINT) that provides answers. Also called Photo Intelligence (PHOTINT), it plays a key role in military strategy and operations.
For example, a GEOINT analyst might analyze terrain to support military operations. The analysis part is where technology comes in. Tools like GIS (Geographic Information Systems) can dig even deeper through data.
GEOINT and You
From enhancing national security to aiding in disaster response, GEOINT’s applications are vast and impactful.
Its reliance on cutting-edge technology and data analysis makes it an ever-evolving field. Those interested have a range of career opportunities.
Did we miss anything about geospatial intelligence? Please let us know in the comment section below.