What is Geofencing? A Guide to Virtual Barriers
A geofence is a virtual geographic boundary. Whether it’s for security, retail or delivery, geofencing gives real-time alerts and increases awareness.
A geofence is a virtual geographic boundary. Whether it’s for security, retail or delivery, geofencing gives real-time alerts and increases awareness.
If you’re looking for topographic maps (contours, place names & hydrography) for the United States, the first place to look is the USGS topo maps series.

Nearest neighbor classification is a powerful approach to classify segmented objects based on specific statistics and training samples chosen by the user.
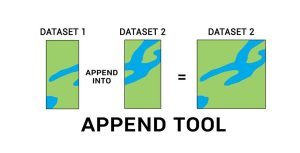
The Append Tool adds data from one or more sources of data and puts it into an existing target dataset, without creating a new dataset.

Geodesy is the field of applied mathematics that studies Earth’s shape, orientation, positions and gravity for the past, present and future.
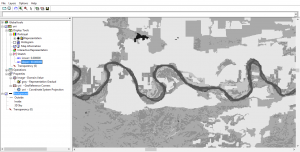
ILWIS is free (GNU license) for users around the world for GIS and remote sensing needs. Here are some of the neat features and developments.
There are several ways to help readers understand map scale and distance. For example, cartographers use scale bars, locator maps, stated and ratio scale.
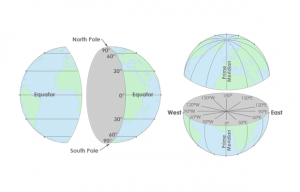
Latitude lines run east-west, are parallel and go from -90 to +90. Longitude lines run north-south, converge at the poles and are from -180 to +180.

ArcScene and ArcGlobe both specialize in 3D. However, ArcScene is for local scenes and ArcGlobe is for global. Find out more differences between 3D software.
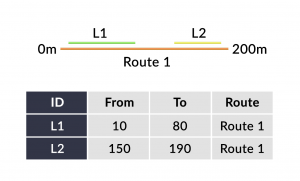
Linear referencing systems (LRS) store relative positions on an existing line feature with m-values for point/line events and linear analysis.