GNSS vs GPS: What’s the Difference?

What are the differences between GNSS and GPS?
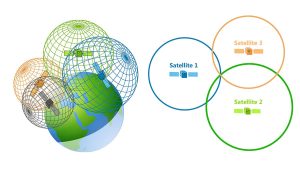
GNSS stands for Global Navigation Satellite System. GNSS is like an umbrella for multiple navigational satellites. Under this umbrella, GPS, along with other systems, finds its place.
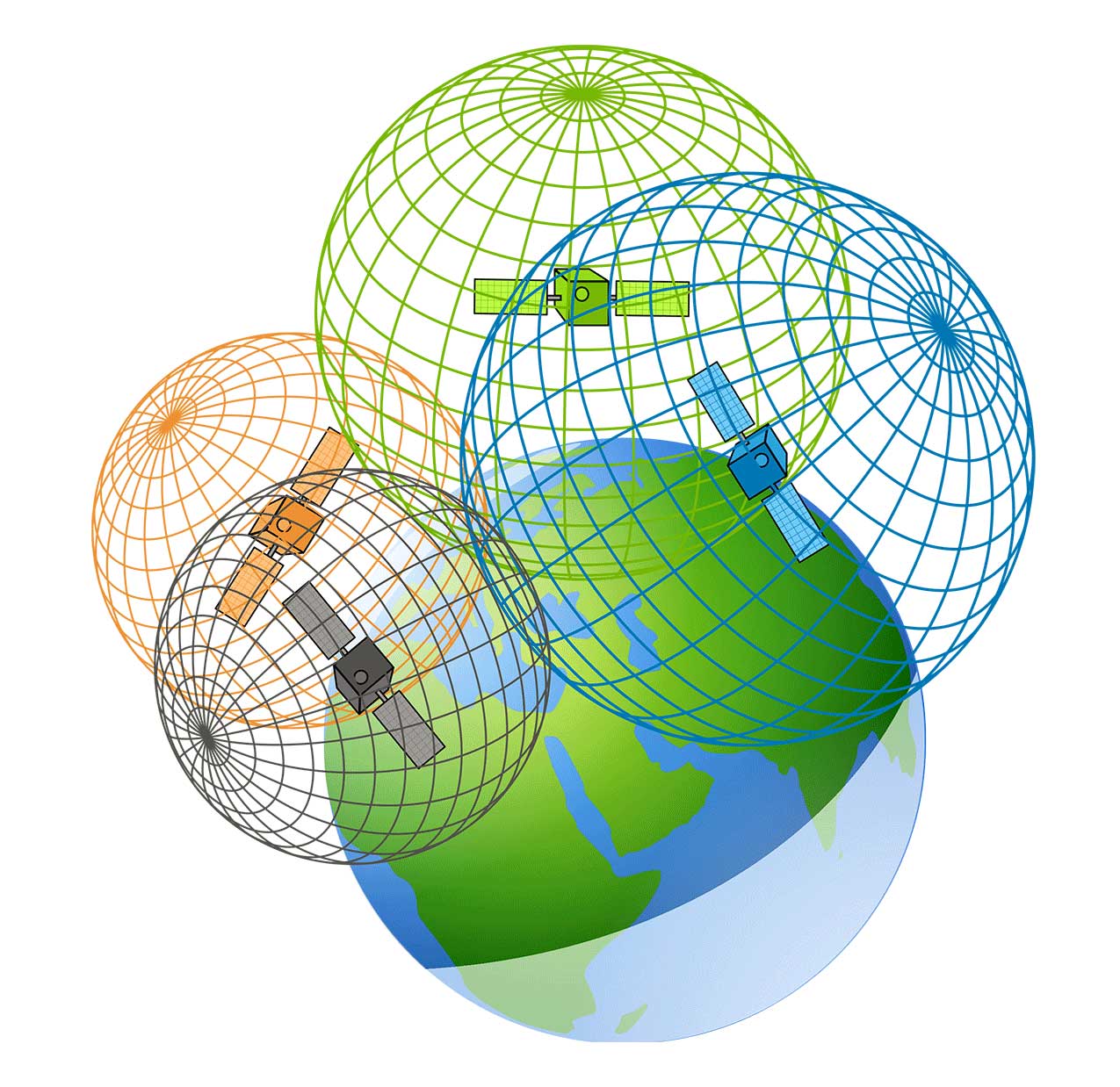
Specifically, GPS is the system developed by the USA, while GNSS encompasses global systems. For instance, it includes Europe’s Galileo, Russia’s GLONASS, and China’s BeiDou. Global Positioning Systems (GPS) is essentially a subset of GNSS.
Let’s say that you have a mobile phone that is GNSS-compatible. This means that you can access other networks beyond the GPS system. Having GNSS-compatible devices adds more reliability and accuracy to your equipment.
What are the advantages of GNSS over GPS?
GNSS provides worldwide location services by leveraging a larger network of satellites. This means GNSS enhances accuracy and reliability.
Below, you’ll find a table that lists the differences between GNSS vs GPS.
| Feature | GNSS | GPS |
|---|---|---|
| Full Name | Global Navigation Satellite System | Global Positioning System |
| Origin | International (multiple countries) | United States |
| Satellite Networks | Includes multiple systems (GPS, Galileo, GLONASS, BeiDou) | Single system |
| Number of Satellites | 100+ satellites from various systems | 31 satellites |
| Coverage | Global, enhanced coverage due to more satellites | Global, but with potentially less precision in certain areas |
| Accuracy | Generally higher because of more satellites | High, but can be limited in difficult environments |
| Applications | Broad usage across navigation, military, scientific research | Widely used in navigation, military, and civilian applications |
| Availability | Access to multiple systems for redundancy and precision | Access to a single system |
| Implementation | Requires receivers compatible with multiple satellite systems | Requires GPS-specific receivers |
| Users | Anyone needing high-precision navigation and timing | Broad usage across various sectors worldwide |
Because of its coverage, GNSS can provide more precise location data. Especially in dense urban areas, GNSS can offer better navigation coverage because it has access to more satellites.
READ MORE: GPS Accuracy: HDOP, PDOP, GDOP & Multipath
Summary: GPS vs GNSS
While GPS operates with its 31 satellites, GNSS benefits from the combined strength. It has access to over a hundred satellites from various systems. This makes its coverage much more vast compared to GPS.
So, while GPS is widely recognized, users with GNSS-compatible equipment can benefit from enhanced accuracy. This collaboration ensures users have the most accurate positioning even in remote locations.
Learn more about Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GPS.gov). Please add your questions and comments about GNSS below.