Parcel Mapping in GIS
What Is a Parcel in Mapping?
In mapping, a parcel is a specific piece of land with defined boundaries. Each parcel is unique, identified by a parcel number. This number helps to track ownership, zoning, and other legal aspects.
For example, when buying a house, the parcel number tells you exactly what land you’re getting. We especially use parcels in planning and development, showing how land is divided.
So, now that you have some background in what a parcel is. How do you create them? That’s what we do in GIS. But first, let’s get into some detail about cadastral data in GIS.
Cadastral GIS data
Cadastral GIS data shows the boundaries and ownership of land parcels. Think of it as a detailed map that tells who owns what land.
It helps in legal matters, such as disputes over land. We also use cadastral data when paying taxes, as it shows property sizes and boundaries.
So, accurate cadastral data is key for managing ownership information. This all begins with the Public Land Survey System (PLSS).
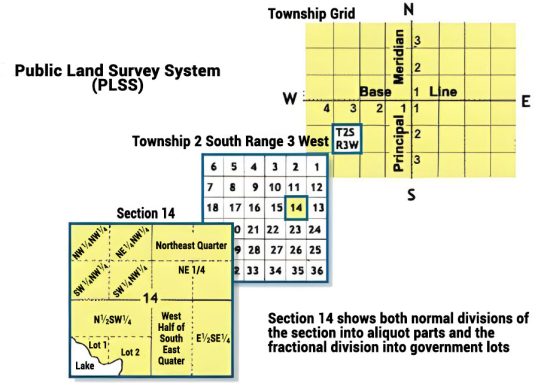
Quarter Sections and Lots
The Public Land Survey System (PLSS) divides land into townships and ranges. Townships are areas of 36 square miles, while ranges are columns of townships. This system makes it easier to describe land locations in the U.S.
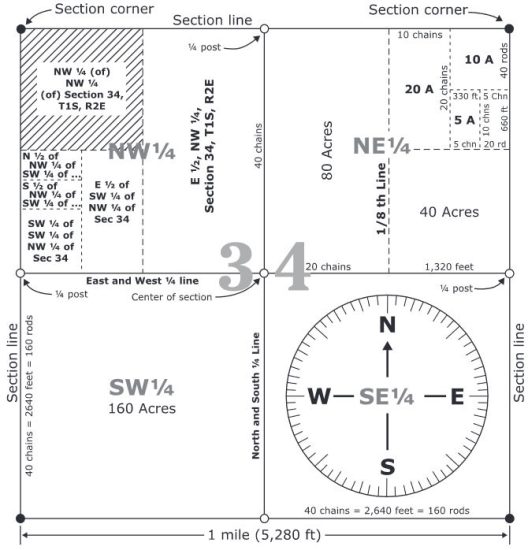
Quarter sections divide a square mile into four parts, each about 160 acres. Lots are smaller divisions within these sections, used for specific land parcels.
We can break down quarter sections into manageable, smaller units for ownership. So, these parcels provide a finer level of detail within the larger township and range system.
READ MORE: Public Land Survey System (PLSS) vs Dominion Land Survey (DLS)
What Is the Role of GIS in Parcel Mapping?
GIS handles complex spatial data, especially for digitizing parcels. With GIS, we can show where parcels are, who owns them, and their land use.
But what are some of the other possibilities for the role of GIS in parcel mapping? Here are some of the other use cases.
1. COGO (Coordinate Geometry)
When it comes to parcel mapping, COGO plays an important role. Surveyors use Coordinate Geometry (COGO) to define land boundaries using traverses and a point of beginning.
GIS professionals rely on COGO to precisely map out the exact boundaries and dimensions of land parcels. This precision is essential for creating accurate and reliable parcel maps.
This level of detail helps in managing property rights and resolving disputes. So, COGO’s role is to provide the needed accuracy in the world of parcel mapping.
2. Parcel Viewers
Parcel viewers are online tools that allow users to view and explore land parcels. They also show parcel boundaries, ownership details, and zoning information.
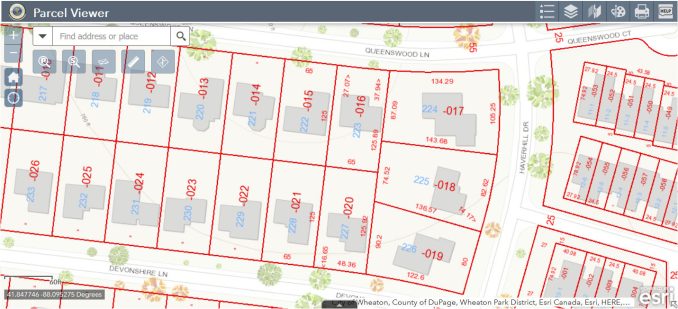
Users can search for a specific parcel by address, owner’s name, or parcel number. A GIS property search makes it easy to access any piece of land.
Even real estate professionals and developers need to know parcel IDs for planning. Parcel viewers provide a convenient way to obtain land-related data without any specialized GIS knowledge.
What is parcel data in GIS?
Parcel mapping is key for managing land and planning cities. In GIS, we use tools like COGO for creating precise mapping. Then, tools like parcel viewers allow anyone to access the data.
So, this about sums up how parcel mapping works in GIS. Do you have any questions about parcel mapping? Please add to our comment section below.