Differential GPS: What It Is and How to Use It

What Is Differential GPS?
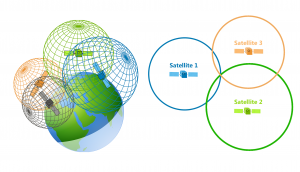
Differential GPS (DGPS) is an important tool in modern navigation. This system uses satellites and reference stations to make GPS receivers more accurate.
This technology helps military personnel and professional surveyors navigate accurately and reliably.
This article will give an overview of DGPS, explaining what it is and how to use it effectively. We will cover the basics, its components, and what it can do for you.
With this information, you will be able to make the most of your DGPS and get the most accurate positioning possible.
How Does DGPS Work?
Before going into the details of how DGPS works, it’s important to understand how GPS works. GPS is a satellite-based navigation system that has been around since the 1980s. In North America, the US government owns and operates the GPS network, which provides free, accurate data to anyone with a GPS receiver.
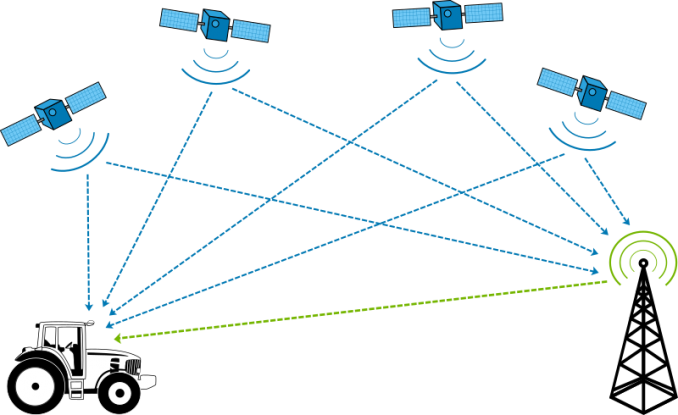
GPS works by receiving information from a network of satellites that are in medium Earth orbit (MEO). These satellites send out radio signals that users can detect with GPS receivers. Then, this information helps calculate a user’s position. From here, GPS receivers use triangulation to pinpoint anyone’s location.
DGPS takes information from the GPS satellites. Then, it adds extra accuracy from ground-based reference stations. So instead of your typical 5-10 meters accuracy, you can get 1-3 meters accuracy with DGPS.
Benefits of Using DGPS
As you’ve already learned, a DGPS is an improved version of the basic GPS. It uses additional reference stations to provide more accurate and reliable positioning data.
The biggest benefit of DGPS is how surveyors can achieve improved accuracy and reliability. In general, a DGPS can achieve accuracies of 1-3 meters, depending on a variety of factors.
This means that survey measurements can be conducted with greater precision and reliability. DGPS is perfect for surveying, construction, navigation, mapping, and engineering purposes.
Components of a DGPS System
Here are some of the critical components of a DGPS system:
1. REFERENCE STATIONS: A network of ground-based reference stations is installed throughout the area. The DGPS system leverages this network of stations. These reference stations contain very accurate clocks. They receive signals from the satellites and compare them to their known position. Any discrepancies found are then sent out as corrections to users of the system. Reference stations are also known as fixed receivers or known points.
2. GPS RECEIVERS: A mobile GPS receiver is the primary component of the DGPS system. First, it receives GPS signals from satellites and decodes them. Next, the receiver calculates the user’s position. This is based on the information received from the satellites, which includes those from the reference station. This is how it obtained an increased accuracy.
Conclusion
Differential GPS is a type of navigation system that can provide more accurate data to GPS receivers. The positioning system uses GPS satellites and ground-based reference stations for accuracy.
DGPS helps users improve GPS accuracy by providing more precise data through differential correction. If you work in surveying, engineering, or maritime applications, a DGPS can provide the accuracy you need for success.