Pleiades Satellite Constellation: Spot the Detail
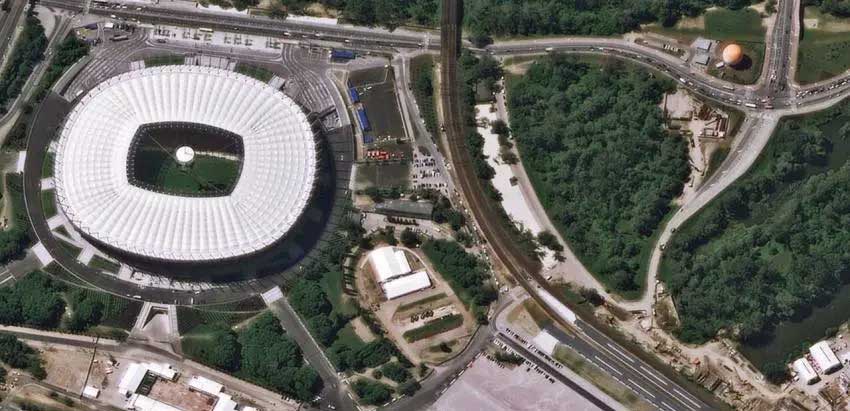

The Perfect Pair – Pleiades 1A and 1B
There is “Pleiades” as in the seven sisters in Greek mythology. There’s also the far, far away star cluster “Pleiades” – which earned its name from Greek mythology. But today we’re here to give you the scoop on the “Pleiades” satellite constellation.
In 2011 and 2012, the Pleiades constellation entered orbit with a pair of two satellites – Pleiades 1A and Pleiades 1B. They share the same orbital plane as SPOT-6 and 7 giving daily revisits over any point on the globe.
The Pleiades satellite tag team is agile. They provide global coverage of the Earth’s surface equipped with high-resolution, multispectral sensors.
Here’s everything you need to know about the Pleiades satellites:
Pleiades Satellite Timeline
The French-Italian ORFEO program built the Pleiades satellite constellation. But France and Italy are not the only end-users of Pleiades satellite data. Spain, Belgium, Sweden, and Austria also are users of this system.
First, Pleiades 1A was launched on December 17, 2011. Pleiades 1B entered orbit on December 2, 2012. With launches almost a year and 90° apart from one another, Pleiades 1A and 1B share the same orbital plane with daily access to every point on Earth.
The Pleiades satellites succeed in a big way because of their agility:
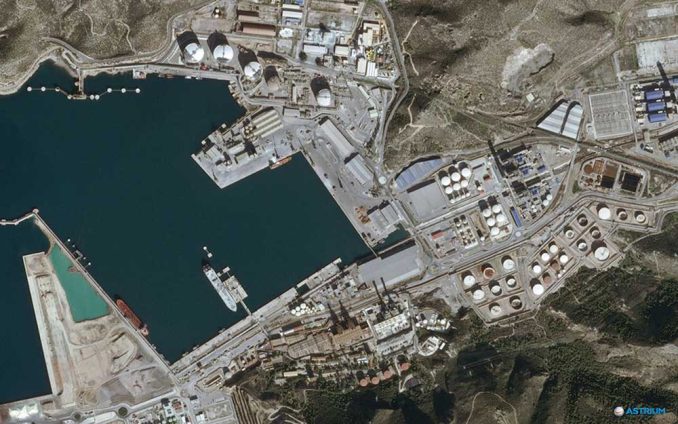

They have the versatility to minimize programming conflicts because of their state-of-the-art image processing chain. They require only six-hour notice before image acquisition – ideal for crisis mapping. Because of its ability to input multiple programming plans per day, this makes Pleiades satellites very responsive to specific user requirements.
- CNES launched Pleiades 1A from the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana on December 17, 2011.
- CNES launched Pleiades 1B from the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana on December 2, 2012.
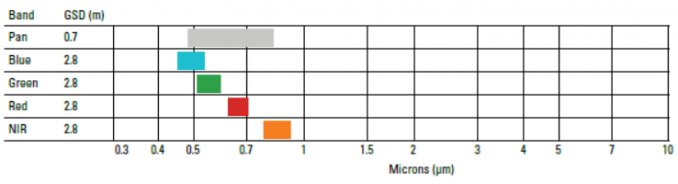
Pleiades Bands and Ground Resolution
Pleiades consists of 5 spectral bands with both 1A and 1B being completely identical to each other. Image acquisition is 50 cm panchromatic and 2-meter multispectral (blue, green, red, and near-infrared).
Pleiades satellite swath width is 20 km. They provide total coverage of the Earth’s surface with a repeat cycle of 26 days. They follow the exact same path as SPOT-6 and 7.
Pleiades Satellite Applications and Case Studies
The Pleiades satellite system was primarily designed for European civil and military. Emergency response and change detection were two key applications for Pleiades satellite data.
But it has evolved into much more than this. Imagery is available for users worldwide and Pleiades satellite data for a wide range of remote sensing applications. For example, land planners, the military, and hydrologists use this type of imagery in a variety of applications.
1. Detecting Coastline Changes
Researchers have found heatwaves, rainstorms and extreme weather severity have increased because of climate change. Shorelines have suffered a more severe onslaught with a higher risk of erosion and river flooding. Coastline changes in particular have seen a dramatic effect.

To monitor these coastline positions, the agile Pléiades satellite can offer a solution because of its unique programming modes, daily revisit frequency, and multiple acquisitions. Using Pleiades’ high spatial resolution data, researchers can quantify coastline change with multi-year observations and compare results.
As a result, planners can rethink affected areas. How can we slow down erosion? How can we restore sites? What is the extent of coastline change? These are the questions that Pleiades satellite data help provide answers to.
2. Unprecedented Responsiveness for Data Acquisition
Where Pleiades really shines is its ability to meet user requests with speed and agility.

When Australia’s Great Barrier Reef needed image acquisition, Pleiades collected it in a single 100-kilometer-wide pass. Pleiades responded with rapid data acquisition in a single working day for 11 different pump stations along the Transco pipeline in eastern Pennsylvania and New Jersey.
Rapid speed. Unprecedented responsiveness. Versatility. Pleiades specializes in meeting user demand quickly with detailed satellite data acquisitions.
READ MORE: 100 Remote Sensing Applications & Uses
Pleiades FAQ
Pleiades 1A entered orbit on December 17, 2012. Then, Pleiades 1B followed almost a year after on December 2, 2012.
Imagery is available from Airbus Defense & Space Pleiades.
The green, red, blue, and near-infrared bands have a resolution of 2 meters. The panchromatic band has a ground resolution of 0.5 meters.
The ORFEO program also developed an open source remote sensing program to tackle common image analysis issues. The ORFEO toolbox software can perform a range of remote sensing functions. This includes radiometry, PCA, change detection, pan sharpening, image segmentation, classification, and filtering.
Conclusion
The Pleiades satellite tag team is agile because it’s able to take user requests with minimal conflicts.
They provide global coverage of the Earth’s surface, with both 1A and 1B in the same sun-synchronous orbit.
They are high resolution from 2 meters multispectral and a 0.5-meter panchromatic band.
To say the least: they are a unique pair of satellites used in a wide variety of applications.
- Image Credit: Pleiades Satellite Products: © CNES 2011-15, Distribution Airbus DS. Courtesy of BlackBridge