25 Must-Know GIS Editing Tools [Cheatsheet]

25 Must-Know Editing Tools in GIS
You can slice, dice, and edit data in a GIS in countless ways. Densify, simplify, smooth, planarize, trim, fillet, divide, and explode… You can do so much!
So, that’s why we’ve created this handy visual guide with the essential GIS editing tools. This is your cheat sheet for creating and modifying GIS data from basic to advanced editing.
If you don’t know about our 15 digitizing tips in ArcGIS Pro, we also suggest that you take a look at this helpful resource.
And if we missed any essential editing tools, don’t forget to let us know with a comment below.
Creating Features
The focus here is starting from scratch and digitizing features. Here are the most common editing tools for creating.
1. Straight Segment
Constructs straight line segments by pointing and clicking each vertex.
2. Streaming Freehand
Generates vertices based on the movement of the mouse pointer.

3. Right-Angle Segment
Squares off edges for all line segments forcing orthogonal (90°) corners.
4. Arc Segment
Adds curvature to line segments by setting a circular or bezier arc.
5. Trace
Creates new vertices by following along an existing feature.
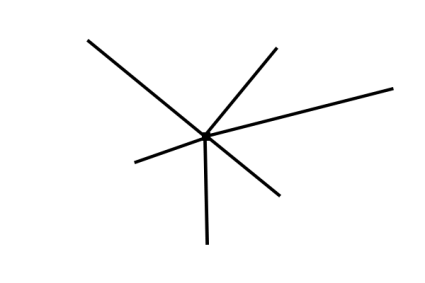
6. Radial
Generates outward directional lines from a center radial point.
Aligning Existing Features
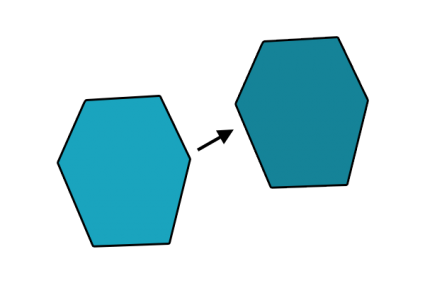
7. Move
Moves features into a new location without the modification of any vertices.
8. Rotate
Spins a feature in a circular motion from a central pivot point.

9. Scale
Resizes a feature proportionately in size by either increasing or reducing it uniformly.
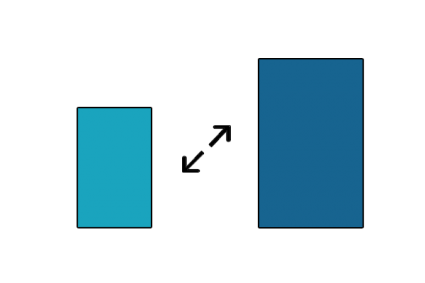
Reshaping Existing Features
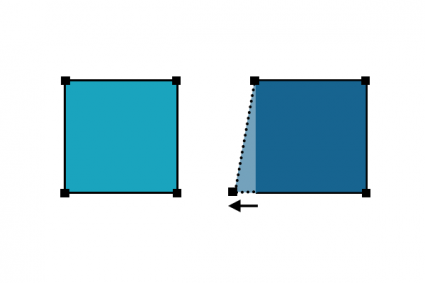
10. Edit Vertices
Selects, adds, deletes, and moves vertices from an existing feature.
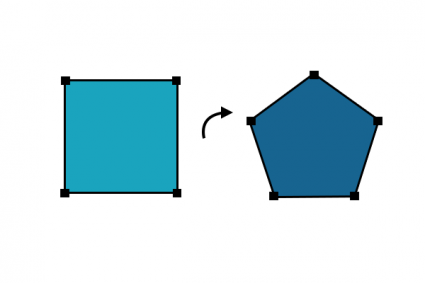
11. Reshape
Updates the vertices from an existing feature using an input digitized line segment.
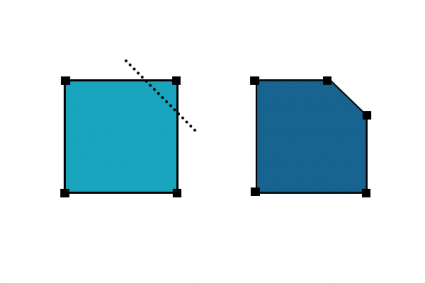
12. Replace
Exchanges geometry from one feature to another feature.
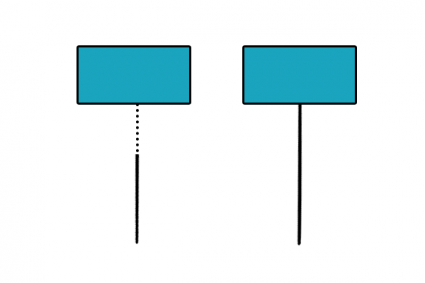
13. Extend
Increases the length of a line to snap to an existing feature boundary.
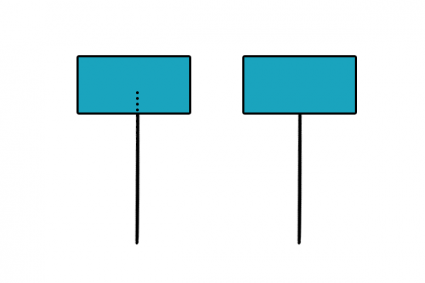
14. Trim
Decreases the length of a line to snap to an existing feature boundary.
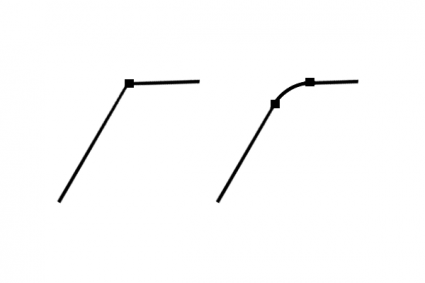
15. Fillet
Adds curvature at the bend of two line segments by creating a circular path.
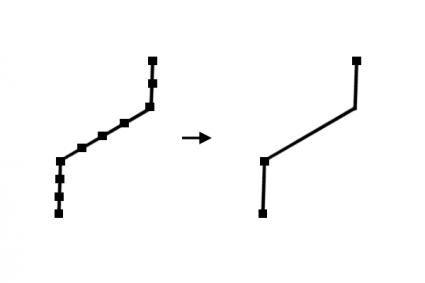
16. Generalize (simplify)
Removes vertices from a line or polygon reducing the complexity of a feature – while maintaining the basic shape.
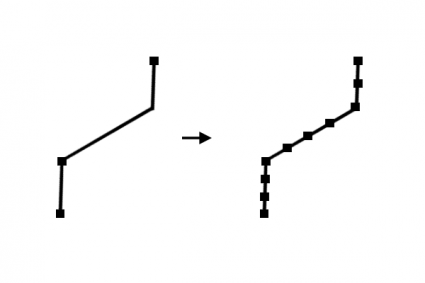
17. Densify
Adds vertices to a line or polygon at a set distance, offset, or angle.
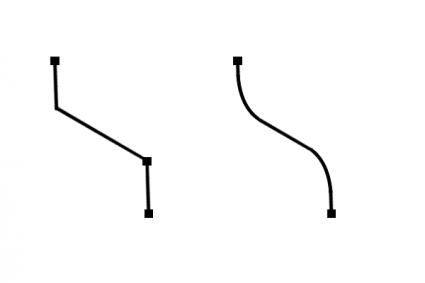
18. Smooth
Inserts vertices at corners to soften corners and reduce jagged edges in geometry.
Dividing and Merging Existing Features
19. Split
Cuts a polygon into separate features based on an existing line.
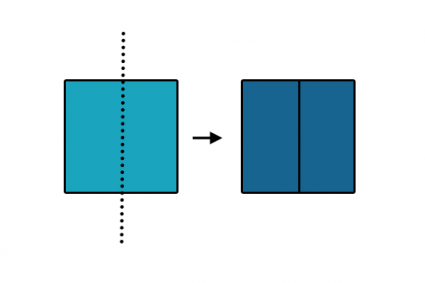
20. Merge
Combines two separate features into a single feature.
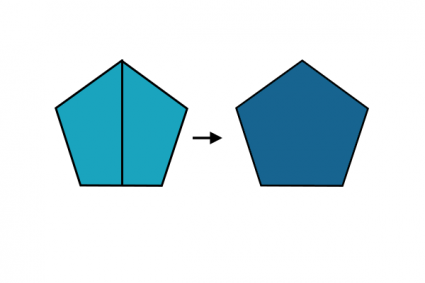
21. Buffer
Widens a point, line, or polygon at a specified distance.
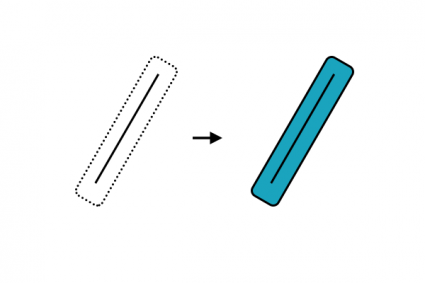
22. Divide
Cuts a line or polygon by distance, percent, or into equal parts.
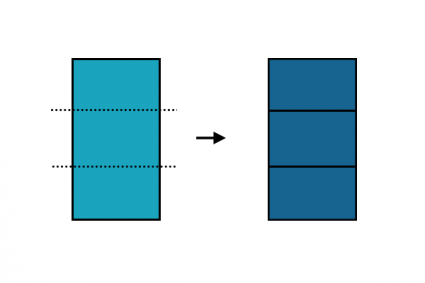
23. Planarize
Splits geometry where features intersect.
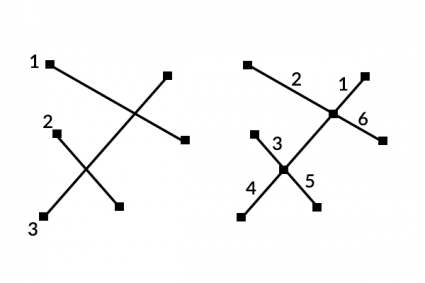
24. Explode
Separates a multipart feature into individual single-part features.
Coordinate Geometry (COGO)
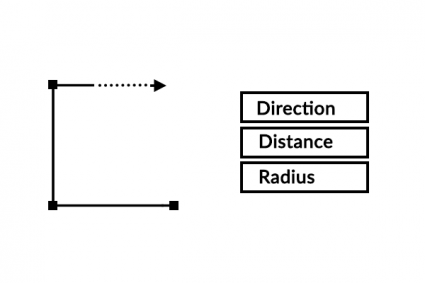
25. Traverse
COGO (Coordinate Geometry) follows along a traveled path (traverse survey measurements) using direction, distance, and radius.
GIS Editing Tools
In GIS, editing tools play a pivotal role in weaving accuracy and detail into spatial data.
As we conclude our exploration of these tools, it becomes evident that their power extends beyond mere data manipulation.
They are the brushes and chisels that refine the canvas of geographical information, enabling us to craft maps that mirror the intricacies of the real world.
With precision, efficiency, and a touch of artistry, GIS editing tools allow us to shape, update, and maintain geospatial datasets.
This ensures that our maps not only reflect reality but also guide decisions and assist in action in a rapidly evolving world.









Thank you for this product
Hi there,
Would you mind sending me any update information.
Regards
Eissa
Instructions on how these tools can be used in a software environment (e.g., QGIS) would have been helpful.
How is this a handy guide? There’s no content, no instructions on how to do these techniques or use these tools, lol.
Thank you. This is indeed a handy guide.