GPS Accuracy: HDOP, PDOP, GDOP & Multipath
Have you ever wondered about your GPS accuracy?
In short, a well-designed GPS receiver can achieve a horizontal accuracy of 3 meters or better.
For vertical accuracy, it can achieve an accuracy of 5 meters or better 95% of the time. Augmented GPS systems can provide sub-meter accuracy.
But it’s still not perfect. What are the sources of GPS errors that can leave you meters off your mark?
What Lowers GPS Accuracy?
Here are possible ways that can lower the accuracy of a GPS receiver.
For example, the geometry, atmospheric conditions, and even nearby objects can reduce the quality of a GPS signal.
Here are the main causes of GPS error and degradation:
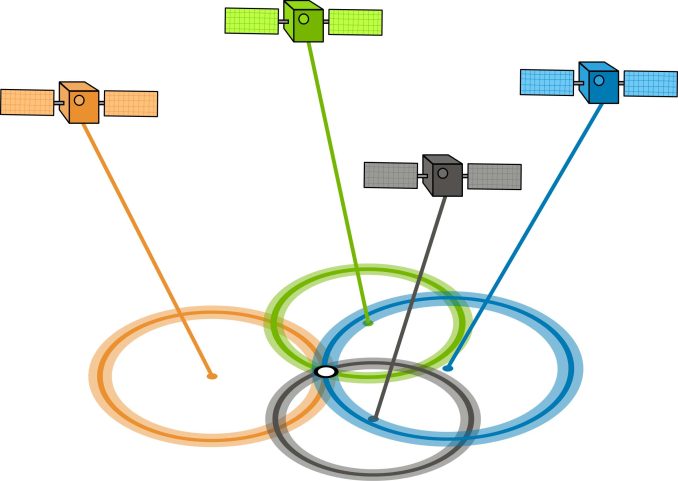
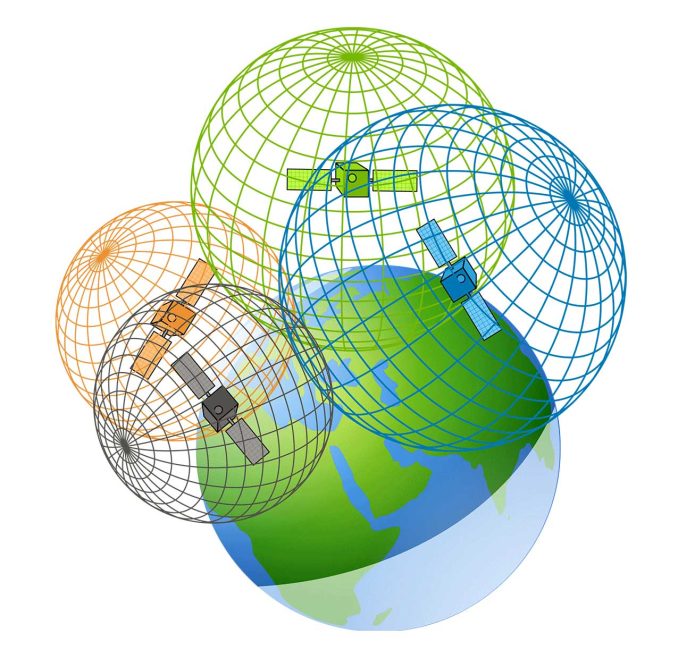
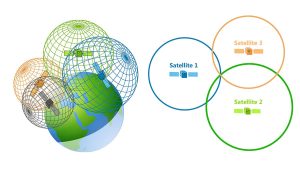
GDOP/PDOP – Geometric/Position Dilution of Precision
GDOP (geometric dilution of precision) or PDOP (position dilution of precision) describes the error caused by the relative position of the GPS satellites.
Basically, the more signals a GPS receiver can “see” (spread apart versus close together), the more precise it can be.

From the observer’s point of view, if the satellites are spread apart in the sky, then the GPS receiver has a good GDOP.
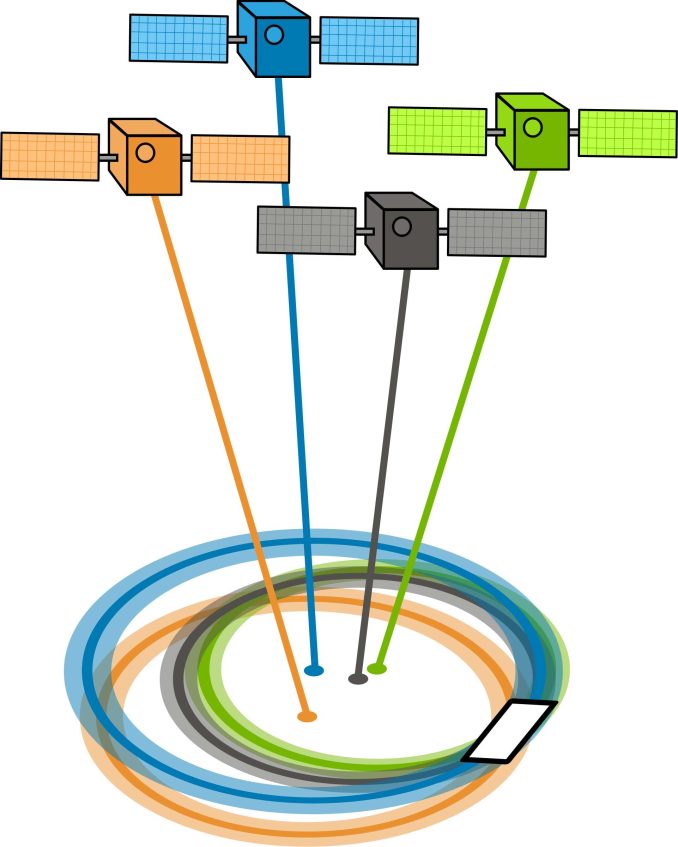
But if the satellites are physically close together, then you have poor GDOP. This lowers the quality of your GPS positioning potentially by meters.
READ MORE: Trilateration vs Triangulation – How GPS Receivers Work
Atmosphere Refraction
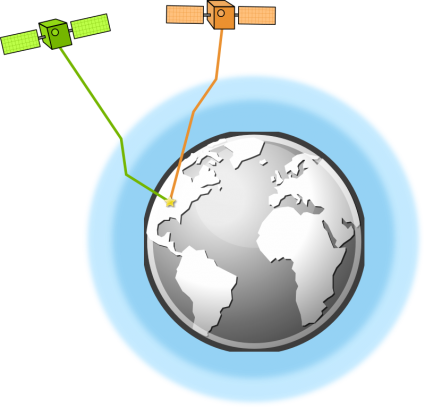
The troposphere and ionosphere can change the speed of propagation of a GPS signal. Due to atmospheric conditions, the atmosphere refracts the satellite signals as they pass through on their way to the earth’s surface.
To fix this, GPS can use two separate frequencies to minimize propagation speed error. Depending on conditions, this type of GPS error could offset the position anywhere from 5 meters.
Multipath Effects
One possible error source in GPS calculations is the multipath effect. Multipath occurs when the GPS satellite signal bounces off of nearby structures like buildings and mountains.
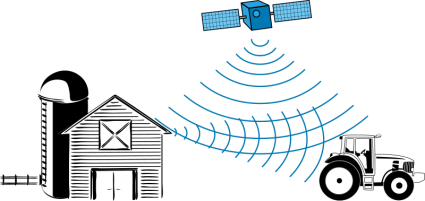
These reflected signals can create interference and introduce errors in the calculation of the receiver’s position, leading to inaccuracies in the GPS measurements.
In effect, your GPS receiver may also detect the same signal twice at different ranges. However, this error is a bit less concerning and could cause anywhere from 1 meter of position error.
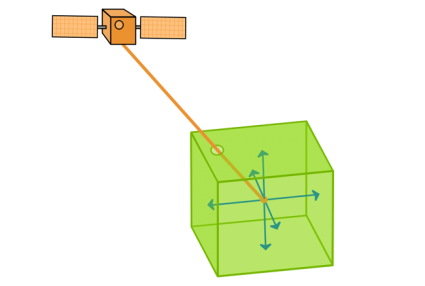
Satellite Time and Location (Ephemeris)
The accuracy of a GPS satellite’s atomic clock is one nanosecond for each clock tick. That’s pretty impressive stuff.
Using the trilateration of time signals in orbit, GPS receivers on the ground can obtain accurate positions. But due to the inaccuracy of the satellite’s atomic clock being synchronized, this can offset a position measurement by 2 meters or so.
The ephemeris information contains details about that specific satellite’s location. But if you don’t know their exact location at a particular time, this can be a source of error.
READ MORE: Geosynchronous vs Geostationary Orbits
Selective Availability
Before May 2000, the United States government added time-varying obfuscated code to the Global Positioning System. Except for privileged groups like the US military and its allies, this intentionally degraded GPS accuracy.
This whole process of degrading a GPS signal is called selective availability. With selective availability enabled, signals added 50 meters of error horizontally and 100 meters vertically. All things considered, this significantly reduced GPS accuracy.
At the time, differential GPS was able to correct. But after 2000, this source of GPS error no longer was much of a concern as the selective availability switch was turned off.
How to Improve GPS Accuracy
Despite all the potential types of errors that can reduce the accuracy of a GPS, there are ways to improve accuracy.
For example, the two major techniques are:
- GPS Differential Correction
- Satellite-based Augmentation System (SBAS)
Let’s take a closer look at how these two GPS correction methods work.
Differential GPS
Differential GPS (DGPS) is more accurate than standard GPS due to its ability to correct errors and inaccuracies in the GPS signals.
DGPS receivers improve accuracy using two receivers because ground-based receivers can take accurate measurements of the error.
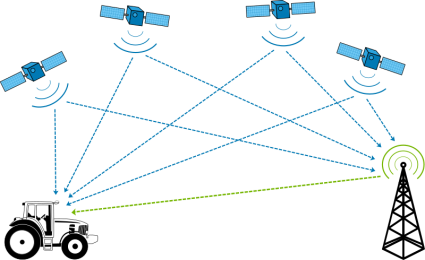
As long as the stationary GPS receiver detects the same satellite signals as your GPS receiver, it can send you correction data based on its precisely surveyed location.
Satellite-based Augmentation System (SBAS)
A Satellite-Based Augmentation System (SBAS) is a regional or global navigation satellite system that enhances the accuracy, integrity, and availability of signals from existing global navigation satellite systems
This augmented system broadcasts the corrected error in real time along with the GPS signal. As a matter of fact, this is the principal idea of a satellite-based augmentation system (SBAS) and can provide sub-meter GPS accuracy.
A Guide to GPS Accuracy
HDOP/PDOP, multipath, and atmospheric effects are some of the common sources of GPS error.
All of these types of GPS errors could lower GPS accuracy.
With the selective availability switch now turned off, we have gained significant improvements in GPS accuracy.
And with techniques like Differential GPS and Satellite-based Augmentation Systems (SBAS), positions can improve to sub-meter accuracy.





Which is a range of good HDOP values.
Thanks
Frank
Typically under 2.5 is considered good for most GPS applications. 1 to 1.5 is really good
Are HDOP, GDOP and PDOP different or the same?
They’re different
PDOP is unitless — It is the ratio between the size of your positional error divided by the error in range from the satellites. If you don’t have good separation between the satellites, the range error bands overlap and you get high PDOP. If the satellites are well separated/orthogonal, then the range errors intersect better and PDOP approaches 1. On a football field with 18yd wide goalposts, there’s a a 2 yard square area that’s 13+/-1 yards from the goalposts (PDOP=~1) and wide 18x2yd crescent band that’s 100+/-1 yards from the goalposts (PDOP=~18)
Lower DOP (Dilution of Precision) value means better positional precision considering wider angular separation between the satellites which is used to determine the GNSS receiver unit’s position.
PDOP/GDOP is the Position of DOP and can be thought of as 3D positioning or the mean of DOP, and most often referred to in GPS accuracy:
HDOP is the Horizontal of DOP; VDOP is the Vertical of DOP, both together give the PDOP or GDOP (Leica and Trimble terminology)
I have a question for you.
I assume that the position of the receiver is fixed in the Cartesian coordinate system.
At this time, are the X,Y coordinates of the satellite position making up the minimum PDOP and the X,Y coordinates of the satellite location making the minimum HDOP the same?
Summary: I’m wondering if the HDOP value is also minimal at the location of the satellite with the minimum PDOP.
I don’t understand…
What is a good PDOP ???
as it approaches Zero it becomes better…the lesser the value of the number the better
Very good and useful for GPS surveyors
So……… While I agree in part – (As I know its much more complex than what this page has) – What would be helpful is a GDOP “good” and “bad” example…
Wonderful simple explanation. Thank you
Gravitational time dilation between the satellite’s clock in orbit and the receiver’s clock on the Earth’s surface, if not corrected for, would mean a c.11km position error. Your satnavs and smartphones know about General Relativity even if you don’t!
Good illustrations and simple explanations, Good.
Very good explanation & very useful
Can we accept the principle that on the basis of “within limits values” of DOP & SNR we may have verified accuracy of position fixing without risk of spoofing?
A good explaination about accuracy of GPS.. thx from Malaysia.. :)
What is the SCALE (units) used to measure PDOP? I understand that PDOP > 6 is undesirable for navigation/landing, however, what does the 6 denote?
The heading includes HDOP but it is not explained. I presume it is the Horizontal Dilution of Precision?
Great, concise and useful