QField: The Field Collection App for QGIS

QField: The Field Collection App for QGIS
QField is an open-source solution for mobile data collection for Android, iOS, and macOS. It’s built by the QGIS team, which we rank as the second most popular GIS software today.
Although it’s relatively new compared to other field apps, it’s still rich in features and free to use. Here are some of the highlights of QField:
- Works fully when offline with customized forms
- Supports various formats and wide symbology
- GPS positioning and camera integration
Today, let’s go through the basic steps in order for you to build customized forms and take your QGIS projects for field collection usage.
How To Use QField
If you’re already familiar with QGIS, then you’ll be quick to familiarize yourself with QField. This is because most of the setup will be in QGIS Desktop.
Basically, you start with a QGIS project. Then, you customize the layers you want. Finally, build a QField package for field usage and sync your data back in the office.
Currently, QField is available for Android, iOS, and macOS.
But let’s get a bit more detail on how to use QField. Follow the steps to get your QGIS project in working order to get it ready for the field.
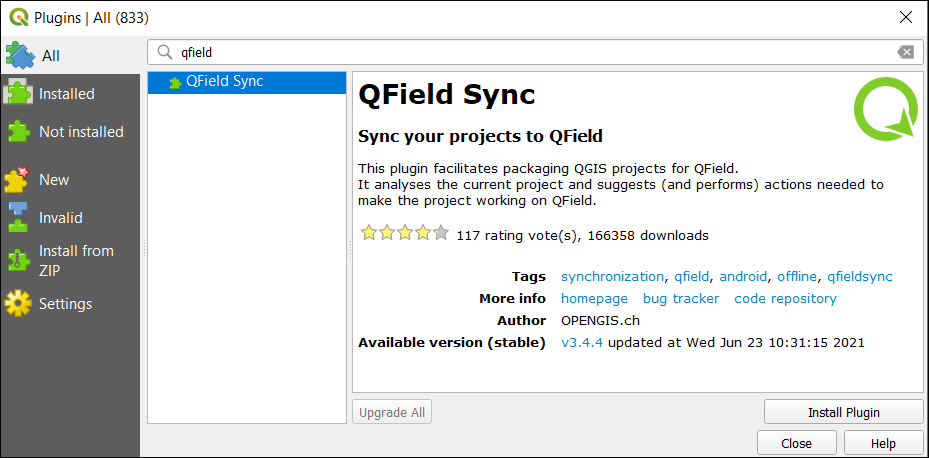
Step 1. Download the QField Sync plugin
The QField Sync plugin analyzes your project and suggests any actions to make sure the project works with QField. This plugin is well-supported by its developers with over 150,000 downloads already.
The main purpose of this plugin is you prepare and package a QGIS project so that it’s compatible with QField. It sets up which layers and base maps you want to use in the field.
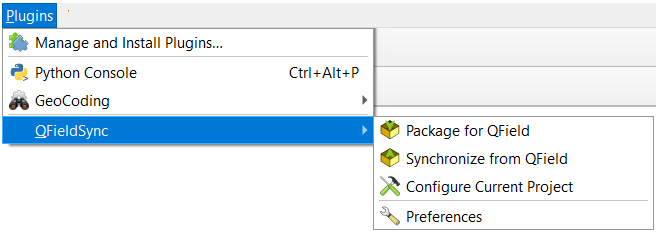
Step 2. Configure your project
First, you will have to configure your current QGIS project. Before you configure your project, you will have to add any layers that you want to be a part of your field campaign.
Once you’ve added them, you can start to configure and set up your QGIS project. All the configurations will be saved to your current QGIS project.
Plugins > QField Sync > Configure Current Project
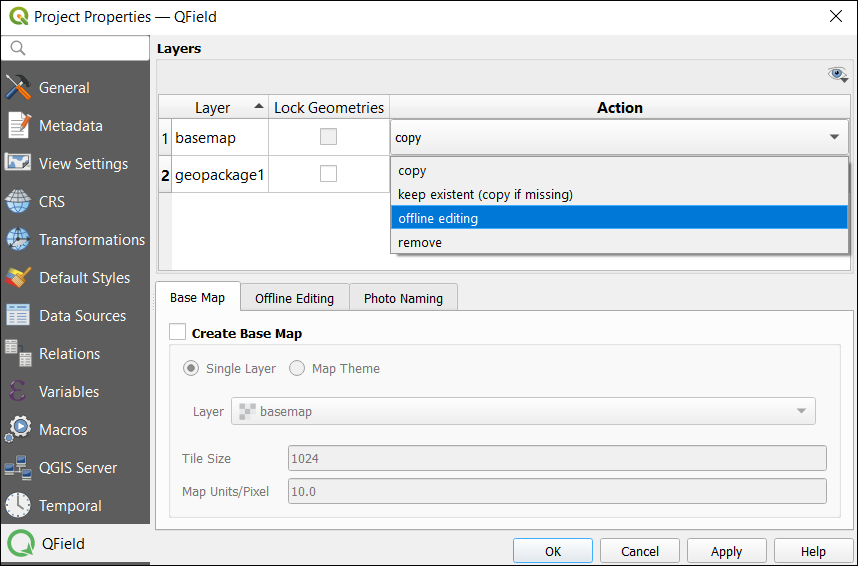
Step 3. Layer configuration
The layer configuration will control the layers that will belong to your fieldwork package. Here are the options you have for layer setup:
- Copy – Copies the layer to the project
- No action – Only for WMS and WFS
- Offline editing – A working copy of the data. After synchronizing any changes after data collection, any changes will be transferred to the main database.
- Remove layer – Layers will not be part of the working copy such as basemaps.
Step 4. Basemap setup
The basemap serves as the underlying layer for your fieldwork. You can set it to your area of interest. You have two options for your basemap.
Layer – This is a great option to generate an offline map of a WMS or raster layer like an ECW.
Map theme – A combination of several layers which can be used as a basemap for fieldwork.
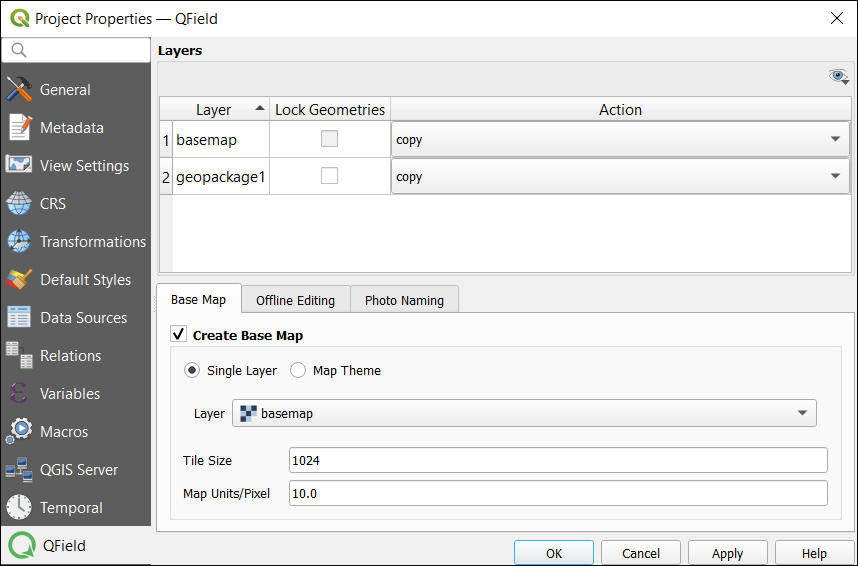
Step 5. Create a QField package
QField syncs with your QGIS project so you can take it out to the field. But before you can take your QGIS project to the field, you have to create a QField package.
In order to package your QGS file, you have to ensure that you’ve completed all the necessary configurations from above. Afterward, you can package it with the QGS file and associated data
Plugins > QField Sync > Package for QField
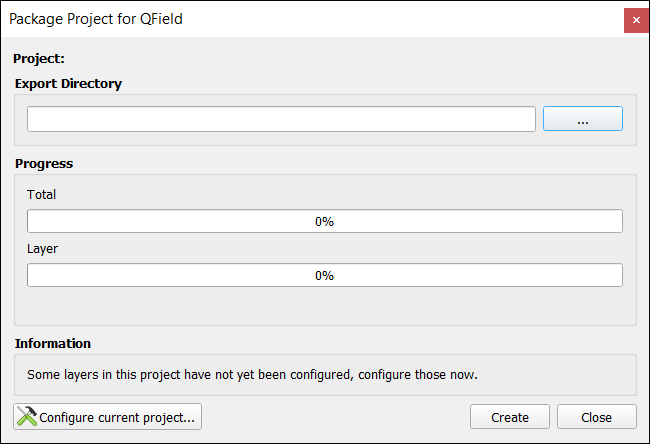
Step 6. Start your fieldwork
The QField Mobile App is available for Android, iOS, and macOS.
First, download the Android App from the Google Play store. Next, you will have to upload the QField package to your mobile phone.
When you go out to perform fieldwork, the QField package will contain all of the layer and basemap configurations.
At this moment, the QField mobile data collection field app has a 4.6-star rating.
Step 7. Synchronize from QField
Once you finish data collection in the field, you can copy the data from your phone and overwrite the project. Any updates in the field including photographs will now become part of the project.
QField Cloud
Datasets can be locally stored or accessed remotely. One of the services that you can use for data collection is QField Cloud.
This type of setup allows you to seamlessly work in sync as a team with more efficiency.
Although it’s still in beta, there’s been a lot of progress in development.
Currently, you can manage teams, design highly customizable forms, and work both online and offline.
Conclusion
Field data collection is generally a tedious activity. Without a mobile collection app like QField, you’d likely enter information into a spreadsheet on paper, then digitize it using GIS software.
That’s not something that most people would enjoy doing on a regular basis. But with a program like QField, mobile data collection can be made easier and more efficient in many ways.
This article introduced you to how to make your field data collection more efficient by using tools like the QField Sync plugin.
It has also helped you understand how to configure your layers and base maps as well as create a QField package for any type of fieldwork.







How can I have general flow chart for qfield app
I am new to Qfield and I have enjoyed reading your article. It is a great introduction to the app.
thanks for the great article, one small correction. As beta packages, qfield is already available for iOS, MacOS, Linux and Windows as well. Just go to qfield.org/get and you’ll see all the links.
Cheers Marco