What is a Basemap?
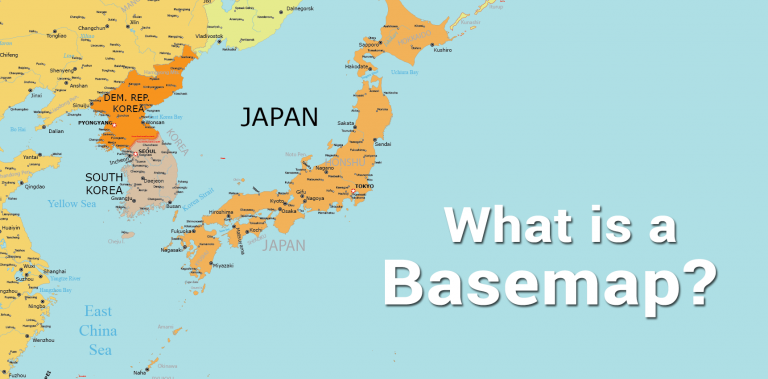
DEFINITION:
A basemap is the background map layer in GIS or mapping applications that provides geographic context for your data.
What is a Basemap?
A basemap is a layer that provides geographical context to the map and other dataset layers above it.
Because reference information is so important in spatial analysis and modeling, almost every map (printed, digital, or web map) includes a background map as a visual reference.
For any map maker, this means that a solid basemap is one of the fundamental building blocks of cartography.
Let’s explore the world of basemaps. What types of basemaps exist? And what are some examples?
Types of Basemaps
Maps always communicate a message. So in order to communicate your message, it is important to choose the right type of basemap.
Although various types of basemaps exist, there are generally just several in use today. Each one has its own benefits and disadvantages when it comes to displaying and conveying information.
Here are examples of basemaps, which describe the types of basemaps and a bit of background in what situations you would use them.
Orthophoto Basemap

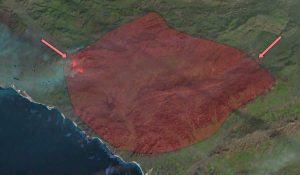
Orthophoto basemaps show ground features with detail from a top-down perspective. They are usually created by satellite imagery, but can also be created with aerial or drone photography.
Its major advantage is that you can see the features of Earth and even measure distances with anything from buildings to streets.
EXAMPLES: Google Satellite Imagery, Esri Imagery, etc.
Topographic Basemap
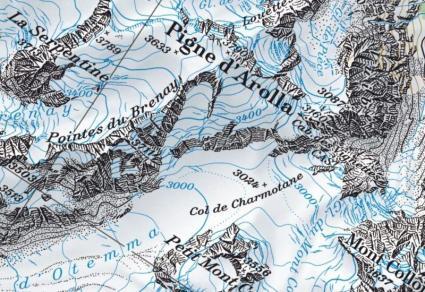
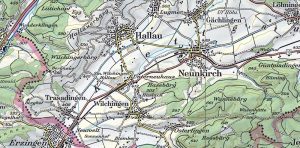
Topography is the underlying foundation of a landscape and can refer to mountains, valleys, and rivers on the surface. A topographic basemap generally includes elevation in the form of contours.
But it can also incorporate natural and artificial features such as administrative boundaries, hydrography, parks, urban areas, and transportation.
EXAMPLES: USGS Topographic Basemaps, Swiss Topo, etc.
Satellite Basemap

Satellite imagery provides users with an aerial view of a location captured from space. This is a useful type of basemap if you want to see any features with an aerial view.
Because satellites orbit in a circular path with repetitive acquisitions, it’s capable of capturing imagery with up-to-date information.
EXAMPLES: Sentinel-2 Views, Landsat Imagery, etc.
Elevation Basemap
A digital elevation model, also known as a DEM, is a digital representation of the elevation surface of the Earth.
Elevation is the vertical distance between the ground surface and an ellipsoid model or geoid. This is useful for depicting any type of construction project as elevation can add extra cost.
EXAMPLES: SRTM Digital Elevation Model, LiDAR DEM, etc.
Contours Basemap
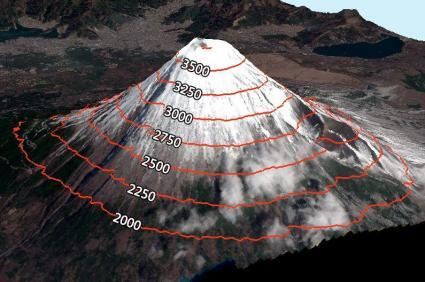
Elevation contours are just another way of showing how elevation changes in geographic locations.
These lines show constant heights of elevation. Contour lines closer together represent steeper terrain. Whereas lines spaced further apart show gentle slopes.
Conclusion
Basemaps are the foundation of any location-based app and most mapping products.
They make it possible for your users to find places of interest near them by giving them reference information in geographic space.
There are many uses for a basemap, and they can come in handy in many different situations to suit your purpose.
Do you have any questions about basemaps? Please let us know with a comment below.





Thanks a lot for giving me basic meanings and definitions on base map!!
I still do not understand the definition and concept of basemap
I still do not understand exactly what a basemap is, and your description of it only tells what it does. Providing geographical context to a map and to other layers above it might mean something to someone who is in the mapping world, but to a layman whose maps are on a single plane, it is not helpful.
Is the basemap the actual map upon which layers of other information is laid? Does it have manmade features? Are roads, towns, etc, named, or even included? Is your illustration at the top of this page a basemap, or is it info overlaid onto a basemap?
I still don’t know, and your answer to “What is a Basemap?” did not answer the question.