Intersect Tool in GIS
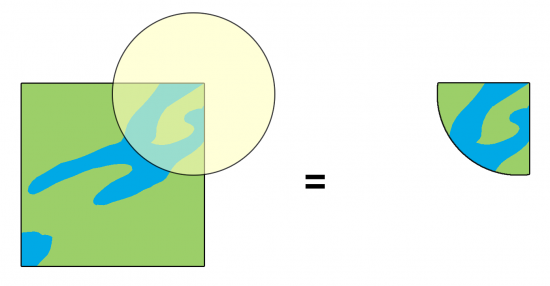
What is the Intersect Tool?
The Intersect Tool performs a geometric overlap. All features that overlap intersecting layers will be part of the output feature class.
But one of the main differences from the Clip Tool is that it preserves attributes from all overlapping layers.
It also allows you to add multiple inputs with different types of data and specify the output as points, lines, or polygons.
Also under-appreciated is the fact that you can run the Intersect Tool on a single feature to find self-overlaps in GIS.
The Intersect Tool works for points, lines, and polygons
If you want to find where points, lines, or polygons overlap, the Intersect Tool is versatile and can work with any of these data types.
For example, two intersecting line layers can create points where they overlap.
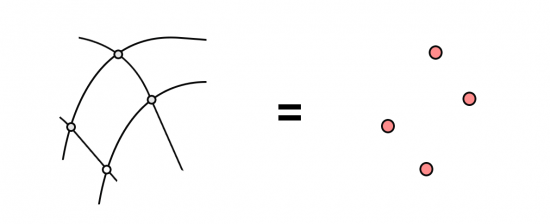
Alternatively, two intersecting line layers can generate lines where they overlap. Ultimately, it depends on how you set the output layer data type for the features you will create.
One of the main advantages of this tool is that you attach the tables from all layers where features intersect. If the point overlaps a territory, it will add attributes from both tables.
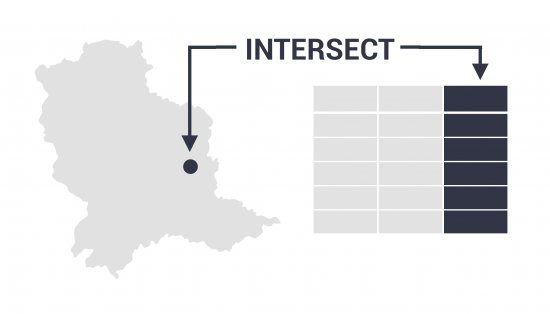
As mentioned before, the Intersect Tool is also great for finding any self-overlapping polygons within a single dataset.
Common errors and troubleshooting
After you run the Intersect Tool, you should spot-check the output to make sure the results are logical.
If it doesn’t work properly, here are some common errors and how to fix them.
REPAIR GEOMETRY – If you see a missing table error, you might have an invalid topology. If this is the case, then you can try to repair its geometry. Alternatively, you can try exporting to a shapefile and trying to run the tool again.
MISSING OUTPUT – Make sure you deselect any features before you run the tool. If you already have features selected, the tool will only run using a subset of selected data.
For troubleshooting, we have a range of common problems and fixes for 999999 errors in ArcGIS.
How to run the Intersect Tool in ArcGIS
In ArcGIS and ArcGIS Pro, the Intersect Tool is part of the “Analysis Toolbox” and within the “Overlay Toolset”.
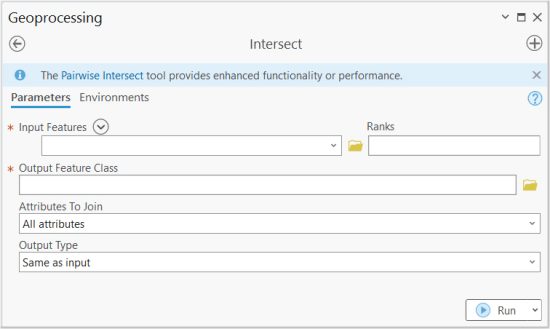
It’s a very basic tool in which you add layers that you want to intersect.
You also set the ranks for how attributes will be ordered in the output feature. And of course, you determine the location and name of the output feature class that you want to write.
How to Run an Intersect in QGIS
For QGIS 3, you can find it in the Vector | Geoprocessing Tool | Intersection.
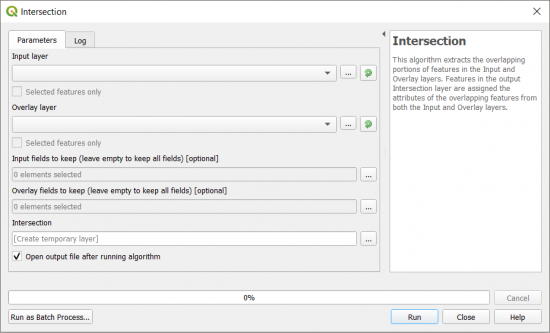
In both GIS software, the main entries are its inputs and output. But in ArcGIS, you can specify the output type as points, lines, and polygons.
In QGIS, you can set if you want to use selected features and if you want to create a temporary output layer.
Summary: The Intersect Tool
The Intersect tool is similar to the Clip Tool, but it’s more versatile for output type (points, lines, and polygons) and finding self-intersecting features.
It’s one of the primary geoprocessing tools in GIS.
Do you have any questions about using the Intersect Tool?
If you do, please let us know with a comment below.










