What is Metadata? (Hint: It’s All About the Data)
DEFINITION:
Metadata is data about data. It describes the who, what, when, where, why, and how of a geographic dataset.
What is Metadata?
GIS metadata is like an instruction manual for data because it describes the who, what, when, where, why, and how of data.
It’s important because it’s the record we rely on to find out how it was created.
That’s why it has to be detailed, dependable, and well-documented. And that’s why we call it the three Ds of metadata.
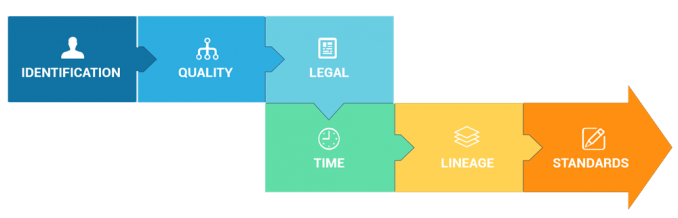
Today, let’s explore step-by-step the anatomy of metadata, like all the necessary information you have to incorporate.
1. Identification

Identification provides a brief narrative of your data. In other words, it summarizes the purpose of your data in a succinct way.
For example, identification assigns the following to your metadata:
- Title – Name of the data set.
- Description – The features in the data set and what they represent.
- Keywords – Adding keywords helps categorize your data with a predefined taxonomy.
2. Contact

The contact information includes details on who developed and made the data available. For example, it includes the following three entities:
- Originator is who developed the data set.
- Publisher assists in producing, editing, and finalizing the end product.
- Distributor has the main focus on making the data available.
3. Quality

Quality explains the accuracy and standards the data set followed. For example, it includes horizontal and vertical positional accuracy:
- Horizontal accuracy evaluates the ground position quality.
- Vertical accuracy exists only when altitude is present.
Quality also evaluates tests of quality including completeness, integrity, and inspections of the data.
4. Spatial Reference

Spatial reference information assigns a geographic extent and coordinate system.
- Projection information includes a projection, datum, and units. For example, UTM Zones and State Plane are common coordinate systems.
- Geographic extent comes in the form of a bounding box, place keyword, or thumbnail.
5. Entity and Attribute

Entities refer to the map data type such as points, lines, polygons, or grids. For example, in a dataset representing cities, each city would be considered an entity.
The purpose of this metadata item is to describe how to represent the spatial information in the data. The entity attributes include a description with a list of valid values and domains.
6. Lineage
Lineage describes the sequence of operations and processes that have been applied to the dataset. This could involve data transformation, projection changes, data cleaning, aggregation, or any other processing that alters the original data.
Additionally, lineage describes who and when was the data processed. For example, it lists the processing steps and responsible parties. Each processing step has a date when it took place so users can track changes. It’s like a changelog listing the evolution of the data from start to finish.
7. Legal

The legal section outlines the constraints for accessing and distributing the data. It describes the liability to assure the protection of privacy and intellectual property.
Metadata includes a security classification that handles the restriction over security concerns. For example, confidential, restricted, sensitive, unrestricted, and unclassified are examples of security classification in metadata.
8. Temporal

It focuses on describing the time-related characteristics of the data, such as when the data was collected, the time range it covers, and any temporal attributes associated with the dataset.
It not only focuses on when the data were collected but how long it’s valid. Plus, it also states the progress such as when there will be future updates. For example, the frequency of updates can be anywhere from daily, weekly, monthly, or annually.
9. Metadata Reference
The metadata reference section is specific to the metadata. This is the individual or organization responsible for creating the metadata. It could be a person’s name, a department within an organization, or any relevant entity.
It also gives a point of contact when there are uncertainties such as how to cite information when used. The metadata reference has a temporal component for when the user created and will revisit it next.
10. Metadata Standard
Metadata standards provide a common framework for describing, managing, and sharing information about GIS datasets in a consistent and interoperable manner.
For GIS metadata standards, geographic data providers follow guidelines from the Federal Geographic Data Committee (FGDC), ISO 19115, EPA, Esri, Inspire, and MEDIN. Each schema was developed to best suit their particular requirements and needs. More on this later.
GIS Metadata as XML
Remember that GIS metadata is just an XML file. Each metadata standard follows a specific schema and markup.
Any text editor can open XML files. When you open a metadata file, it incorporates all the key elements in the markup.
<origin>National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)</origin>
<pubdate>2019/05/15</pubdate>From these two blocks of XML code, you can find that NASA is the originator. Also, the data was published on May 5th, 2019.
Types of GIS Metadata
Several committees from around the world have developed their own guidelines for metadata. In terms of GIS metadata, the most common are as follows:
- ISO 19115 is the guideline from the International Standards Organization (ISO).
- Federal Geographic Data Committee (FGDC) metadata is largely used in the United States.
- Inspire metadata defines standards for 34 spatial data themes for countries in the European Union.
- The EPA metadata editor was developed by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
There are tools to translate content from one metadata standard to another. For example, Esri’s metadata translator can convert it into stand-alone XML metadata.
However, keep in mind that this tool will not carry all fields over. If one field isn’t part of another metadata standard, then it will be missing by default.
The Metadata Song
Now that you have a fairly good idea about metadata, here’s a song about metadata. I don’t know if you’ve ever heard it before…
But just remember that metadata creation might be the most boring task you’ll ever have to do in GIS. So every time you create metadata, remember the song for a bit of extra motivation.