Dissolve Tool in GIS
What is the Dissolve Tool?
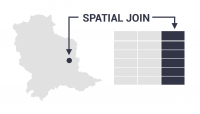
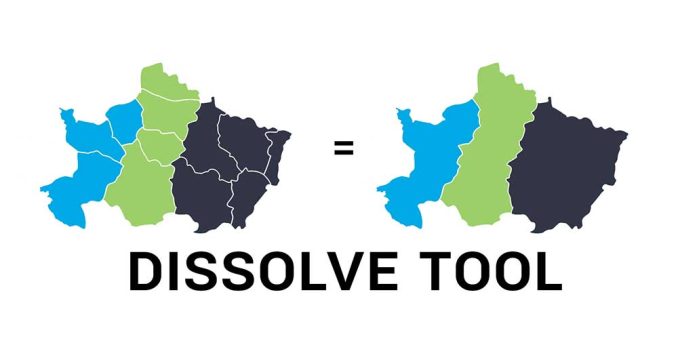
The Dissolve Tool unifies adjacent boundaries based on common attribute values.
Only if neighbor polygons have the same dissolving attribute, then it melts the boundary into one.
Dissolving is mainly for generalization and always simplifies boundaries from a more complex one.
You can use this tool with the three main types of geometry, including points, lines, and polygons.
Dissolve Field and Attribute Loss
As long as you have a dissolve attribute, this determines which features they will amalgamate with.
For example, if you want to dissolve countries into a continent, then you will need a field in your data that specifies the continent.
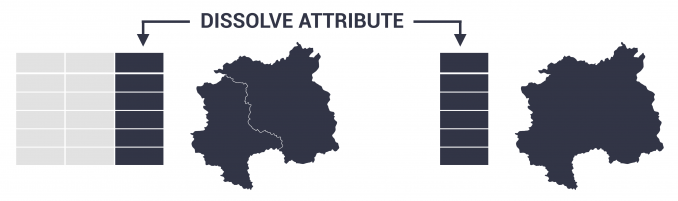
The output will not retain all attributes unless you select the column as a dissolve field. This is why it’s easy to lose information, which isn’t included in the selected fields.
Dissolving is different from the Merge Tool, which puts all the items from multiple datasets into a single dataset. But the key is that merging maintains the boundaries between features.
What are some examples of the Dissolve Tool?
The Dissolve Tool is one of the most common tools in GIS. The highest usage is for cartographic display and data management.
Here are some examples of dissolving features:
In all cases, dissolving features result in more generalization. After running this tool, you can never end up with more records than you started with.
How To Use the Dissolve Tool in ArcGIS
In ArcGIS, you can access the Dissolve Tool through the Data Management Tools in the Generalization Toolset.
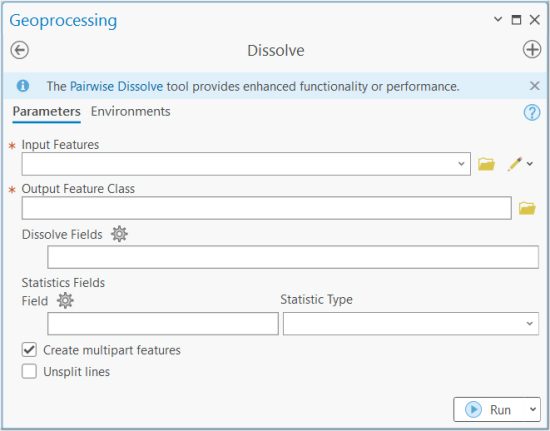
The main option is setting the field(s) in which you want to dissolve. Be very careful about which fields you dissolve as it can make a big difference on the outputs.
There is also an option to summarize with a statistics field. By selecting any statistics, you can summarize values such as by sum, mean, minimum, or maximum.
How To Use the Dissolve Tool in QGIS
If you’re using QGIS, you can find this tool in the Vector | Geoprocessing Tools | Dissolve.
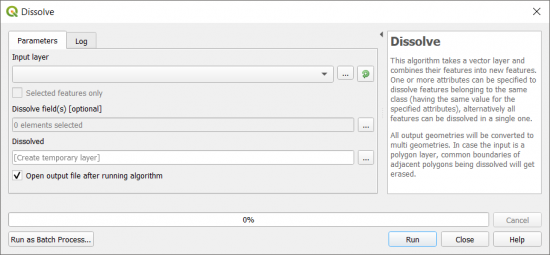
The main difference between the two tools is that you can calculate statistics in ArcGIS. But in QGIS, you can run statistics after the process.
One of the nice options in QGIS 3 is that you can create a temporary layer that’s stored in memory. This is good for examining your dissolve before creating an output file.
Summary
The Dissolve Tool is one of the most common tools and is excellent for generalizing data in GIS systems.
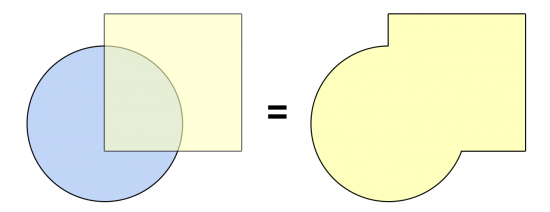
The main purpose is that it burns neighboring borders based on a common attribute. But you can also use it for creating multipart features for lines and points.
It’s a common geoprocessing tool for generalizing and can be found in our Periodic Table for Spatial Analysis.
What are some examples of how you dissolve features? Have you experienced any errors with this tool? Please let us know with a comment below.