5 Types of Network Analysis in GIS

What Is Network Analysis?
Almost everyone has needed a type of network analysis in their life.
For example:
Here are the 5 most common types of network analysis.
1. Point-to-point analysis
A point-to-point analysis is the most common routing problem. It consists of a set of points to find the most optimal route based on specific criteria.
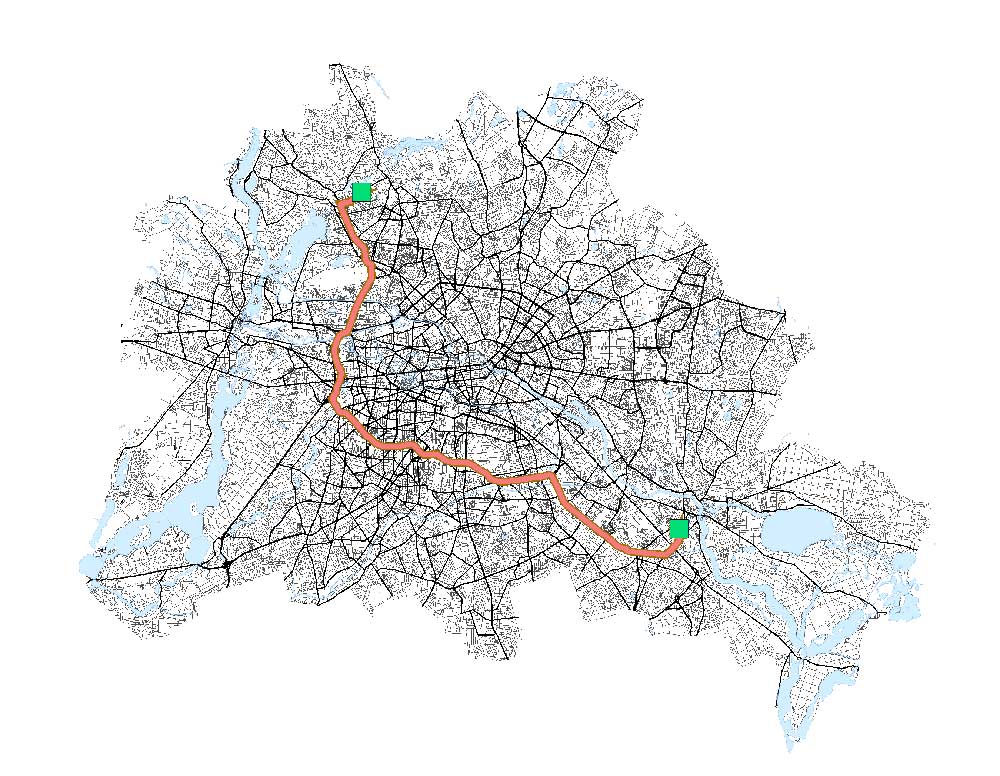
Find Nearest – Where is the closest destination? It finds the nearest destination based on a starting point with multiple potential destinations.
Shortest Distance – What’s the fastest route? This analysis accumulates all distances, as you travel out from one point to the other. Then, it finds the route with the least distance.
Fastest route – Which route takes the least amount of time? This network analysis takes into account speed limits, road classification, and other costs to determine the least travel time.
Other types of point-to-point analysis include the most eco-friendly, scenic, and winding routes. Each type of network analysis generates directions from origin to destination.
It can also include the capability to select the mode of travel such as emergency vehicles, trucks, pedestrians, transit, or cycling.
2. Finding Coverage
In this type of network analysis, drive-time areas correspond to the distance that can be reached within a specific amount of time.
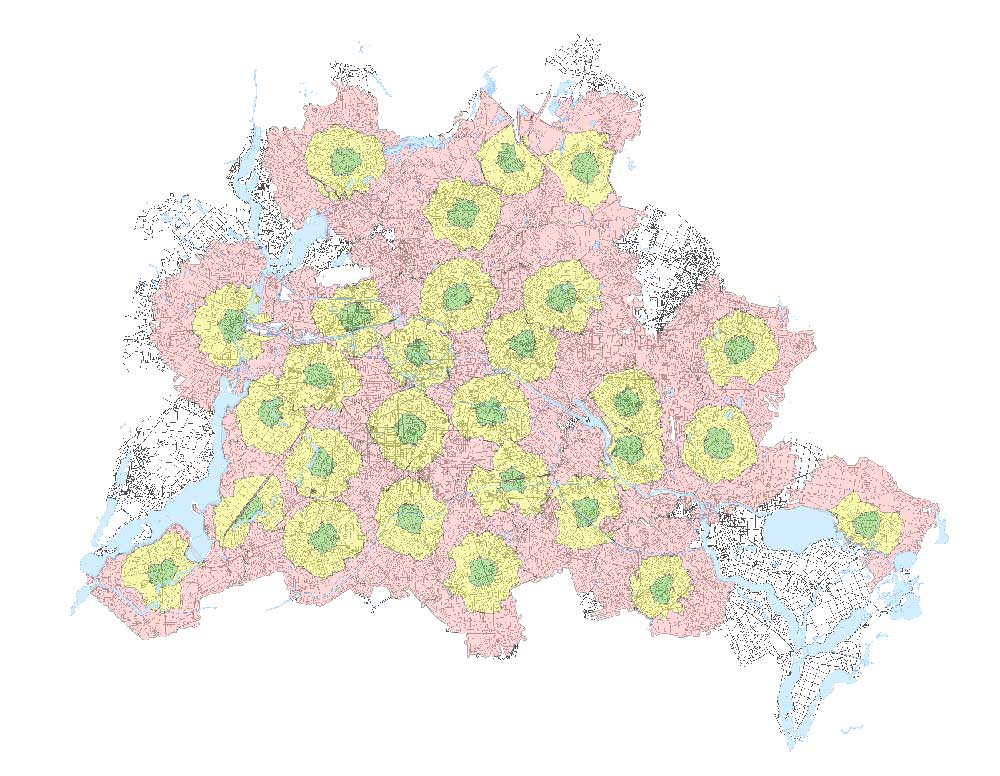
Service Areas – Which houses are within 5, 10, and 15 minutes from a fire station? This type of network analysis also can understand where businesses cover and if there are any gaps.
Drive-time areas are different from buffers because they take into account a street network. Buffers can cross water bodies but drive-time areas can only cross water when there’s a bridge.
READ MORE: How to Find Service Areas with ArcGIS Network Analyst
3. Optimize Fleet
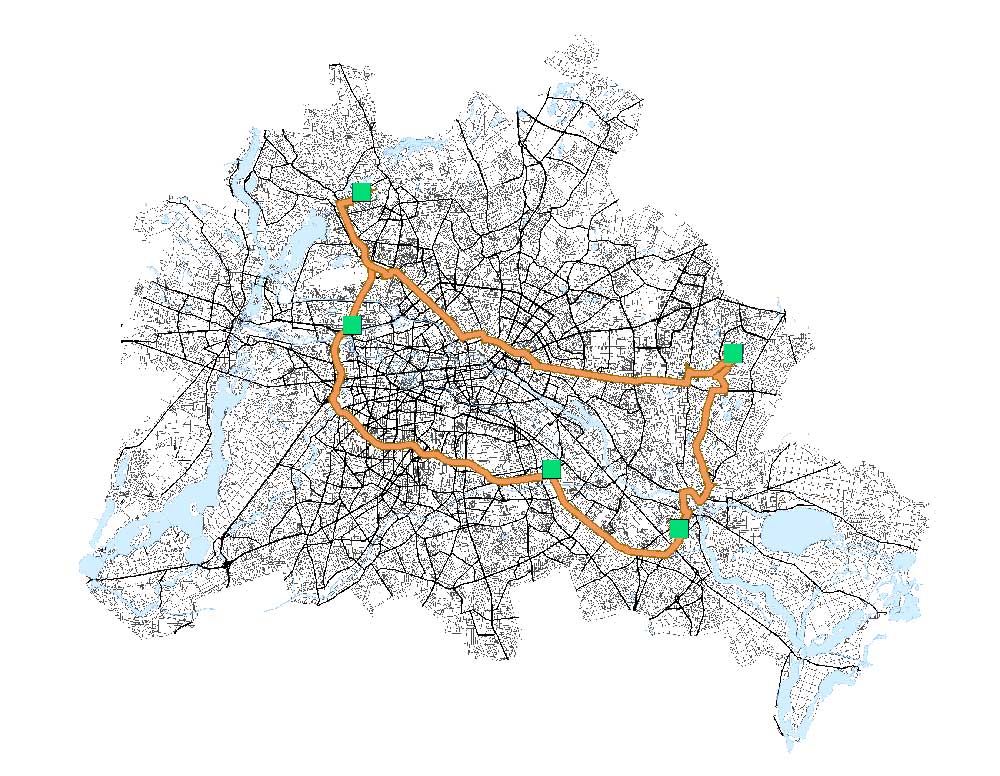
This tool is ideal when your main goal is to service a set of orders in the traveling salesperson problem. Also, you can best minimize the overall operating cost, by managing sets of vehicles and drivers.
Optimize Fleet – The purpose of this network analysis tool is to find the most efficient route for delivery, repair, transit, or any type of fleet service.
For example, a furniture company might want to use several trucks to deliver furniture to homes. Alternatively, a fleet might want to schedule their weekly visits, including all the logistics.
4. Select Optimal Site
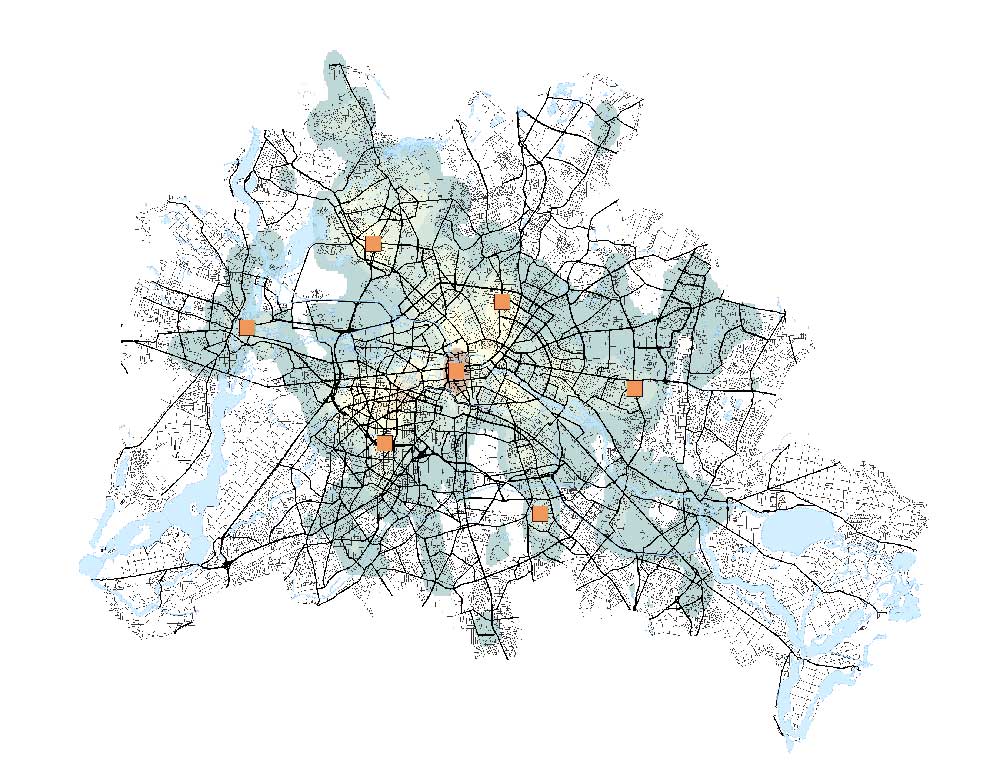
This is where GIS truly shines in transportation. Optimal site selection takes into account the demand to locate the best location given several facilities.
For example, it can help decide where to build new hospitals depending on existing hospitals and the available demand.
Location-allocation – This network analysis tool helps business owners pinpoint the optimal location for their store. It can also compare with competing stores to target market share.
READ MORE: Why Is Location-Allocation Optimal For Site Selection?
5. Origin-Destination – OD Cost Matrix
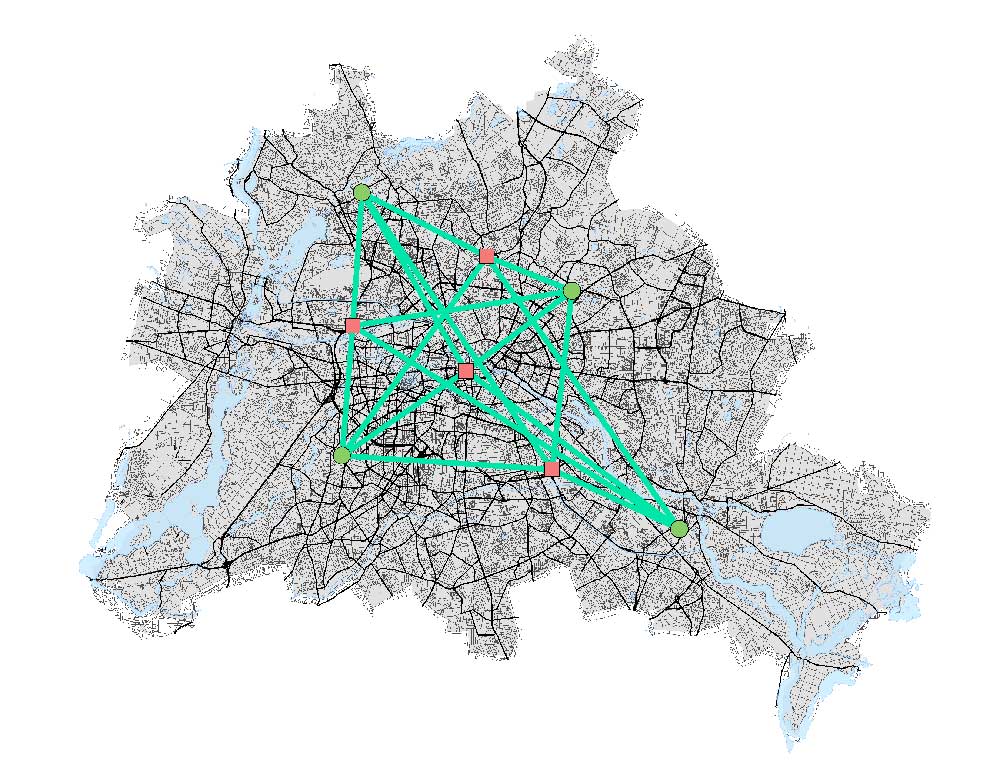
In ArcGIS, this is the OD Cost Matrix, which measures the least cost path from multiple origin points to multiple destinations.
OD Cost Matrix – This type of network uses two sets of locations to find the distances between all of the locations in two sets.
For example, it can list the routes and directions for all stores and warehouses. In emergency dispatching, one set of locations consists of the incident, and the other set is all the available fire stations.
Network Analysis Software
Network analysis consists of a set of analysis techniques used with networks. By using geometric networks, you can understand how anything flows within them.
Rules dictate how objects move through the network. Each type of analysis follows these rules, influencing the outcome of the selected route or result.
Here are some of the most common GIS software that supports the analysis, creation, and use of networks:
ArcGIS Pro – As part of the Esri ArcGIS suite, the Network Analyst extension supports the maintenance and analysis of network datasets. This toolset works primarily with road networks – by building and analyzing network data sets with nodes, direction, and connectivity.
QGIS 3 – In QGIS, the Road Graph Plugin works for point-to-point analysis like the shortest route. As part of QGIS, the GRASS GIS toolset supports various types of network analysis.
READ MORE: 35 Differences Between ArcGIS Pro and QGIS 3










