Viewshed Analysis in GIS
Viewshed analysis is a 3D technique that enables us to visualize and assess what is visible from a specific vantage point within a landscape.
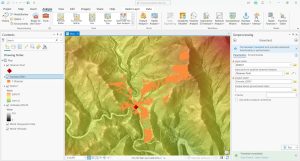
Viewshed analysis is a 3D technique that enables us to visualize and assess what is visible from a specific vantage point within a landscape.
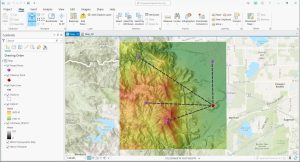
Line of Sight analysis is a geospatial technique that allows us to assess the unobstructed view between two points within a given landscape.

Raster analysis is the process of analyzing spatial information contained in grid datasets such as soils, land cover, elevation, and more.

The Periodic Table for Spatial Analysis lists 90 tools for quantifying, finding patterns, and predicting outcomes in a geographic context.

Zonal Statistics uses groupings to calculate statistics (sum, mean, maximum, etc) for specified zones like countries, watersheds or parcels.

A mosaic combines multiple raster images to obtain a seamless raster. We show you how to mosaic raster datasets in ArcGIS and QGIS.
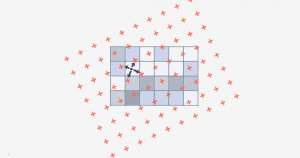
Bilinear interpolation (or bilinear resampling) uses 4 nearest neighbors to generate an output surface when you resample or reproject rasters.
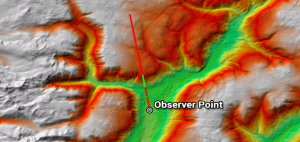
While line of sight determines obstructed and unobstructed on a line, a viewshed dictates surrounding areas as visible or non-visible from an observer POV.
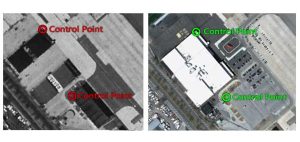
Learn how to georeference with precision in this georeferencing guide. Add control points in two images, select a transformation and check your RMSE.

In the case of a semi-variogram, closer things have less variability and are similar. While things farther away are less predictable and are less related.