Line of Sight in GIS
DEFINITION:
Line of Sight (LOS) is a tool used to determine whether one point on the map can “see” another, based on elevation and obstacles.
What Is Line of Sight Analysis?
Line of sight analysis is a method to check if there are any obstacles between two points in a landscape.
In GIS, understanding the line of sight has various applications. This includes everything from urban planning to military strategies.
By understanding visibility, line of sight helps us find optimal locations and obstructions.
This article explains the concept of line of sight in GIS. Plus, it helps our understanding of spatial relationships.
Line of Sight Analysis
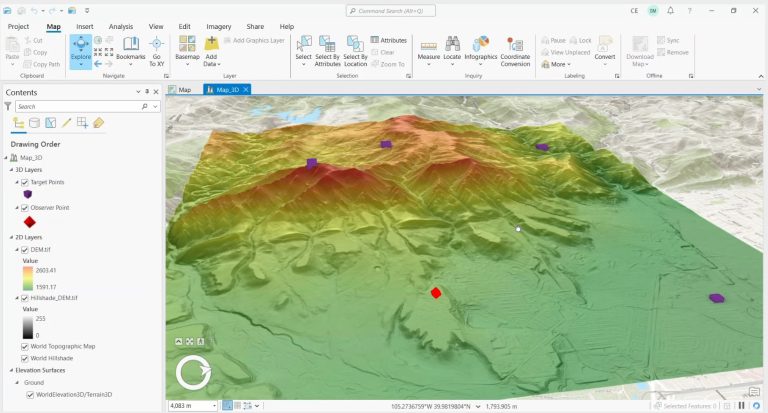
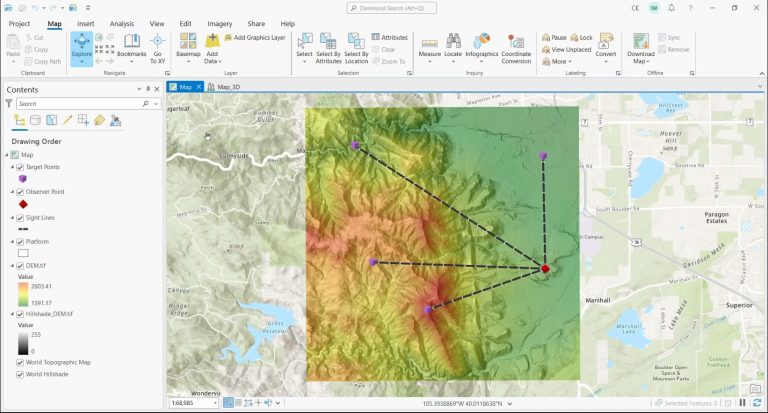
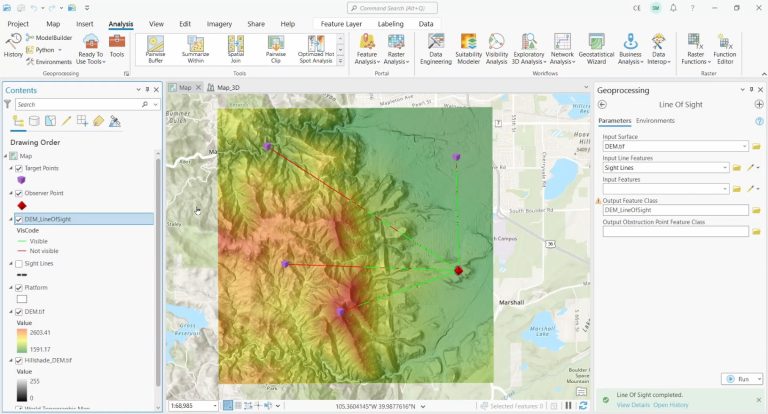
The base data for a “Line of Sight” analysis is an elevation dataset. This is the only way to ascertain visible and obscured regions.
What this tool does is it displays visibility by color-coding segments along the line. Visible areas are in green and non-visible areas are in red.
As a 3D analysis tool, this technique offers an observer a visual representation of visibility along their line of vision.
READ MORE: Viewshed Analysis vs Line of Sight
Line of Sight Applications
Line of sight analysis in GIS has diverse applications across various fields. This is because of its ability to assess visibility between two points in a given landscape. Some notable applications include:
1. Urban Planning
Line of sight analysis helps urban planners determine optimal building locations. First, it can help preserve scenic views. Secondly, line of sight can assess the impact of new developments on existing landscapes. Finally, it can plan pedestrian-friendly pathways that maintain visibility and safety.
2. Telecommunications
Telecom companies use line of sight to select suitable locations for communication towers and antennas. This can help ensure clear signal propagation and minimize signal obstruction by terrain or buildings.
3. Military Strategy
The military uses line of sight analysis to evaluate vantage points, identify potential hiding spots, and assess strategic positions. This can aid in understanding how terrain features affect visibility.
4. Environmental Impact Assessment
In environmental studies, line of sight analysis helps assess the visual impact of projects like wind farms, solar installations, or mining operations. It allows stakeholders to evaluate how structures might alter the visual landscape.
5. Security and Surveillance
Line of sight analysis assists security professionals in identifying blind spots, optimizing camera placements, and understanding how structures and vegetation impact surveillance coverage.
These applications highlight the importance of line of sight analysis. Similar to a viewshed analysis, it optimizes resource allocation and improves spatial planning across various industries.