3D Analysis Tools in GIS – Bend It in 3D
3D Analysis Tools in GIS
3D analysis has been a growing trend in GIS because it’s a better representation of the real world.
It’s not only for a pretty picture. For some types of problems, 3D analysis is sometimes the only way you can solve them.
There has also been an explosion in 3D data types driving this demand. For example, LiDAR, BIM, UAV, textured meshes, photogrammetry, boreholes, IoT, augmented reality, InSAR, space-time cubes, and indoor mapping are examples of 3D data.
But what kind of tools are available? Here are some of the common types of 3D analysis in GIS.
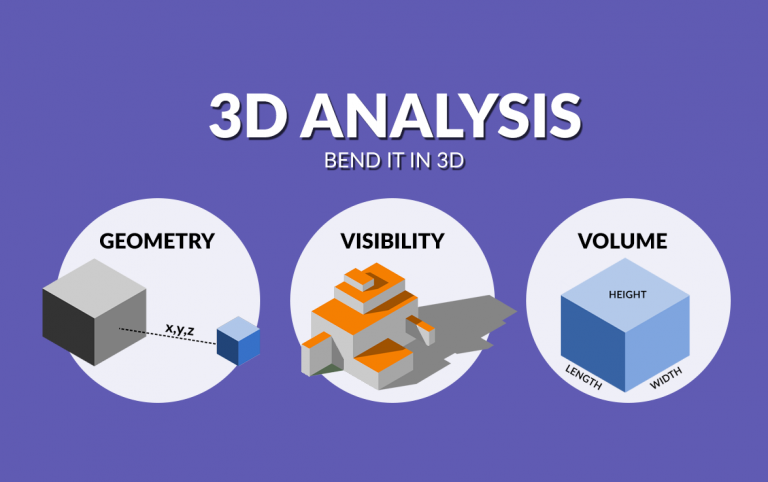
3D Geometric Analysis
These 3D tools perform overlay and proximity analysis in 3D based on the geometry of the features.
1. Buffer 3D
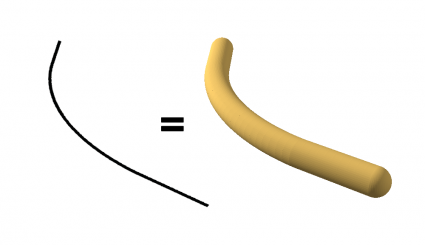
The 3D buffer tool builds a 3-dimensional buffer around points, polylines, or polygons.
2. Intersect 3D
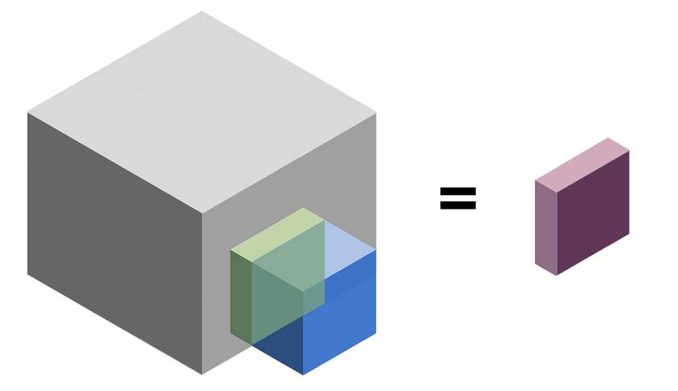
The 3D intersect tool performs the intersection of 3-dimensional features maintaining overlapping features.
3. Near 3D
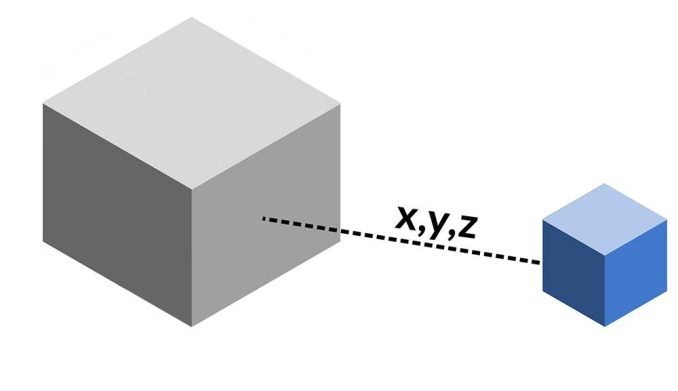
The Near 3D tool measures the distance in three dimensions from each input feature to the nearest feature.
4. Inside 3D
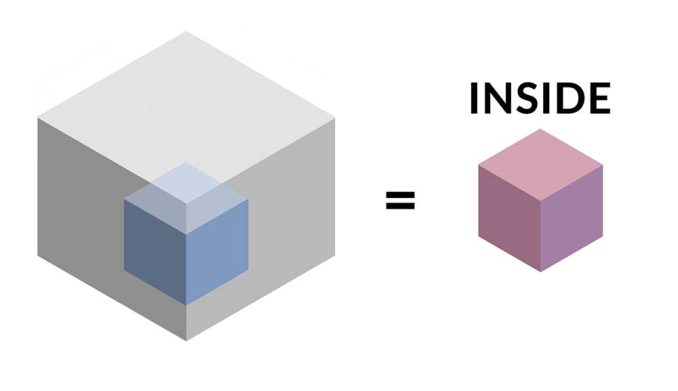
The Inside 3D tool identifies any features that are inside or partially inside a 3D feature class.
5. Union 3D
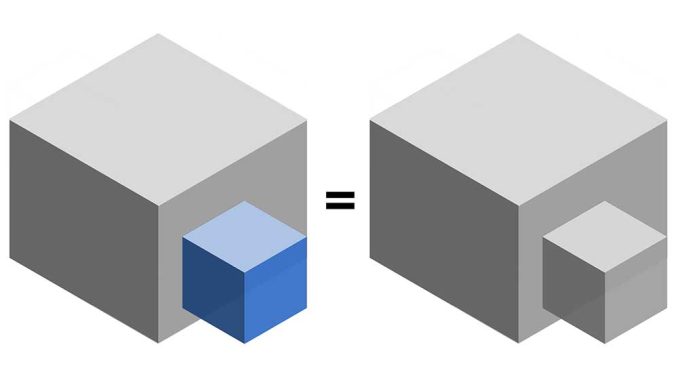
The 3D union tool combines input data layers into a single composite layer, preserving the boundaries and attributes from all input features.
Visibility and Points of Observation
This group of 3D tools focuses on what’s visible from an observer’s point of view. These tools are standard in the military, city planning, and other industries.
6. Line of Sight
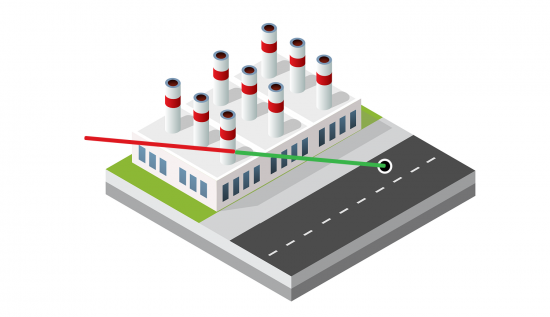
The line of sight tool identifies obstruction and non-obstruction parts of a straight line from an observer.
7. Shadow Analysis
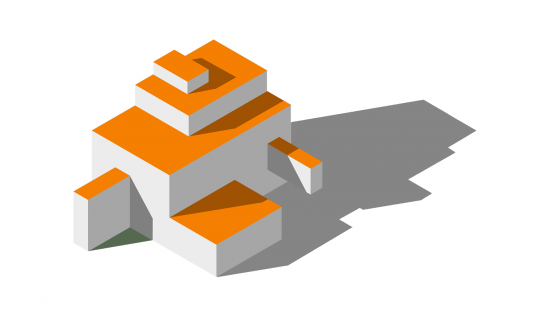
Shadow analysis evaluates the amount of shadow and impact of the proposed building in an urban setting.
8. Skyline
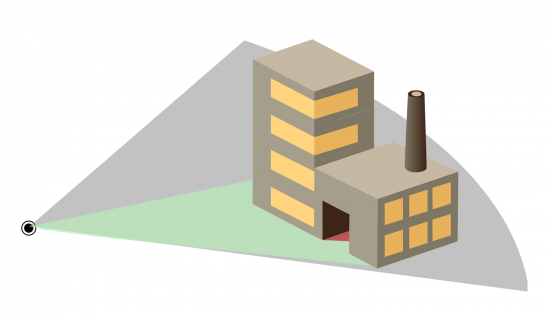
The skyline tool displays visible and obstructed areas like a 3D fan pointing from an observer’s point of view.
9. Viewsheds
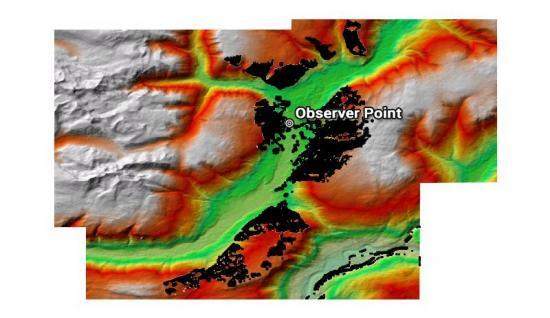
A viewshed determines locations visible to an observer in all directions with the output as a visibility raster.
READ MORE: Line of Sight vs Viewsheds
Surface and Area Calculations
This group of 3D analysis tools focuses on measurements of surfaces and volumes.
10. Volume
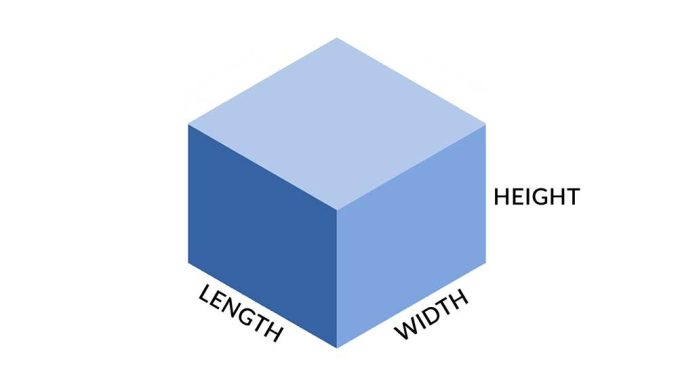
The volume tool calculates the amount of space above or below a reference.
11. Surface Area
The surface area tool calculates the total area of the surface of a three-dimensional object.
12. Cut/Fill

The cut/fill tool identifies the areas and volume of the surface that have been modified by the removal or addition of surface material.
Summary: 3D Analysis Tools
Although 3D analysis adds an extra level of complexity, it’s a better representation of reality.
But it’s not just for its powerful visualizations, 3D analysis adds a third dimension.
By adding 3D data, you can explore visibility like viewsheds and line of sight. Also, there are all sorts of neat geometrical analysis tools.
How do you use 3D in GIS? What types of 3D analysis do you perform? Please let us know with a comment below.