QGIS Cloud: Free Web Maps in QGIS
How To Use QGIS Cloud
QGIS Cloud is a way to publish your Desktop GIS maps to the internet as a web map. As a spatial data infrastructure (SDI) on the internet, QGIS Cloud provides all of the following:
- Publish web maps on the internet
- Manage data through the cloud
- Share information and print maps
QGIS Cloud enables you to publish maps and data on the internet without the need to own your own server. With QGIS Cloud, you can build professional maps and publish them to the cloud through QGIS Desktop.
Today, let’s explore QGIS Cloud, the online platform designed for QGIS 3. It’s free to use but how much does QGIS Cloud Pro cost? How do you publish a web map?
QGIS Cloud Free vs QGIS Cloud Pro
You can publish your maps free of charge on the internet and make them available to anyone through the free version of QGIS Cloud. But the free version has limitations for database size, SSL, personalizations, and usage.
If you want to limit access to your web maps, QGIS Cloud Pro is the only way to do that. That means that QGIS Cloud Pro is the ideal solution for researchers, decision-makers, students, and all who want to build web maps and set restrictions on access.
Here are the differences between the free version of QGIS Cloud and QGIS Cloud Pro:
| Feature | QGIS Free | QGIS Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Free | 65 Euro/month (70-75 USD/month) |
| Usage | Unlimited public maps (Non-commercial and non-government uses) | Commercial |
| Database | 1 PostGIS database (Max 50 MB, max 10 concurrent connections) | 10 PostGIS databases (Max 500 MB) |
| Daily Database Backups | No | Yes |
| Editing Through Web Feature Services | No | Yes |
| SSL support | No | Yes |
| Viewer personalization (logo, colors, etc) | No | Yes |
QGIS Cloud Plugin
To get started, you have to search for the QGIS Cloud plugin in the repository within QGIS Desktop. Next, you will have to download it, install it, and turn it on.
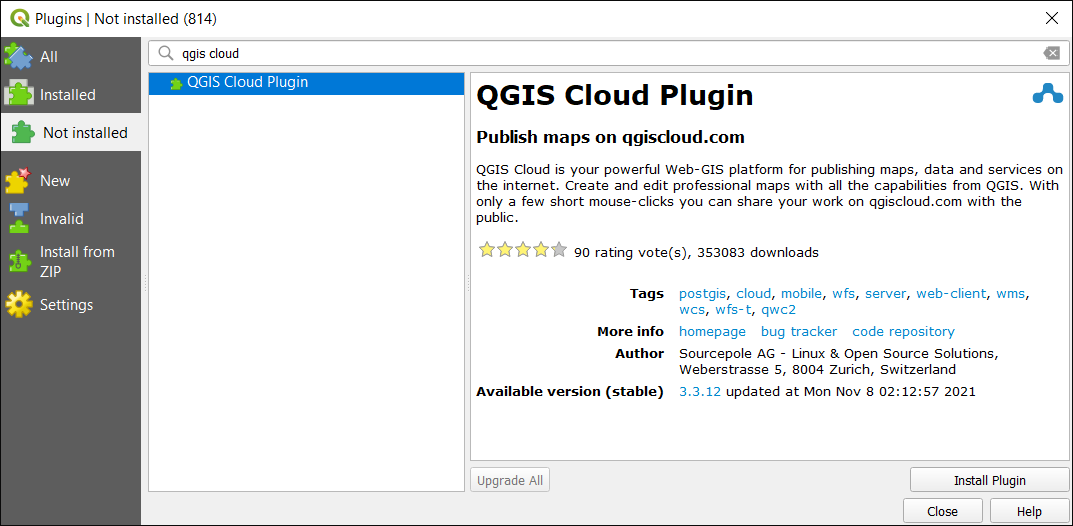
Once you’ve downloaded and installed the QGIS Cloud plugin, you will have to create an account with QGIS Cloud. Enter in your username, email, and password. Next, you will have to confirm your account.
Now, you will have to log in with your username and password in QGIS Desktop. You will have to create a database on their server. The “Upload” tab shows your layers and data source.
Remember that if you are using the free version, you will have a limit of 50 MB. But from here, it’s a matter of customizing your QGIS Desktop map to fit your preferences. For example, you can add OSM data and this will be included in your web map as well.
Web > OpenStreetMap Layers
Once you’re OK with the layers on your canvas, it’s time to upload your data. This stage takes layers from your hard drive and uploads them to a database in QGIS Cloud. Overall, this gives access to it online from a web server.
Save as QGS Project. Afterward, you can publish the map. Once it’s published, it gives you a web URL to your map on the QGIS Cloud website. There are also options to turn layers on and off, the identity tool, and map tools for measuring. You can also sync QField to QGIS Cloud.
READ MORE: QGIS Tutorial: How To Use QGIS 3
QGIS Cloud Web Maps and Examples
Here are some examples of the different types of web maps you can build in QGIS Cloud. It’s not as flexible as ArcGIS Online, but it still has some of the basic functionality.
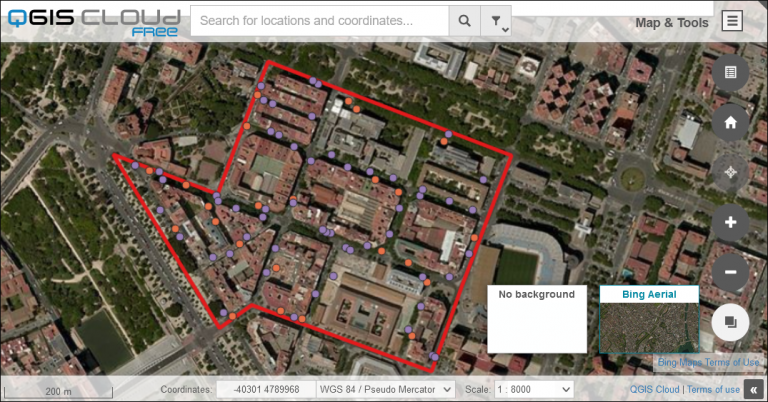
For example, here is an example of a web map that contains basic vector polygons with slight transparency. You also have the capability to change your basemap to your liking.
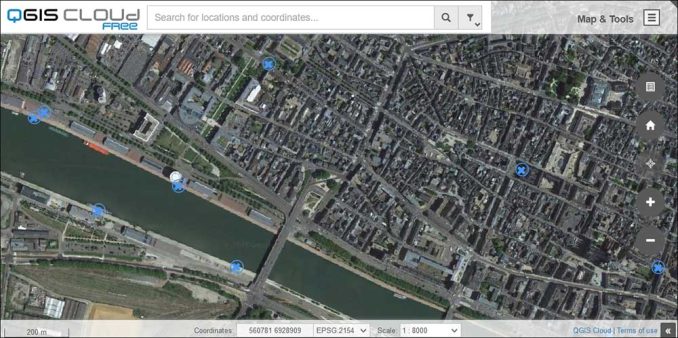
Here is another simple web map that shows basic point symbols. But this web map includes Google Satellite Imagery as a basemap. Plus, it includes several other widgets on the right-hand side of the map as well.
QGIS Cloud: Free Web Maps in QGIS
QGIS Cloud is a plugin for QGIS that provides services for storing and creating web maps to publish on the web. It makes it easy to manage your data and is an excellent cloud solution for those who don’t want the hassle of managing their own web server.
With QGIS Cloud, you have quite a bit of flexibility by adding various widgets and types of layers to your web maps.
If the free version is not sufficient for your needs, there is also the option to upgrade to QGIS Cloud Pro which can restrict access to others, give you more storage, and the capability to customize the interface even more so.
Have you ever used QGIS Cloud? What did you think of it? Please let us know with your comments below.








