DLG, DRG and DOQ: USGS GIS Formats
USGS Vector and Raster Formats
The USGS has been a driving force in GIS. As part of the USGS topographic maps, they’ve designed formats that date back to the 1980s.
USGS Formats like DLG, DRG, and DOQ are standardized geospatial data formats that were commonly used for mapping and imagery in the past
This is just when Geographic Information System was emerging from its roots. What you’ll discover in this article are three USGS formats used to store GIS data.
USGS File Types
These three USGS file types are:
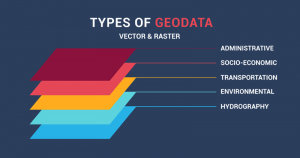
- DIGITAL LINE GRAPH (DLG) are vector files generated on traditional paper topographic maps. For example, this includes townships & ranges, contour lines, rivers, lakes, roads, railroads, and towns.
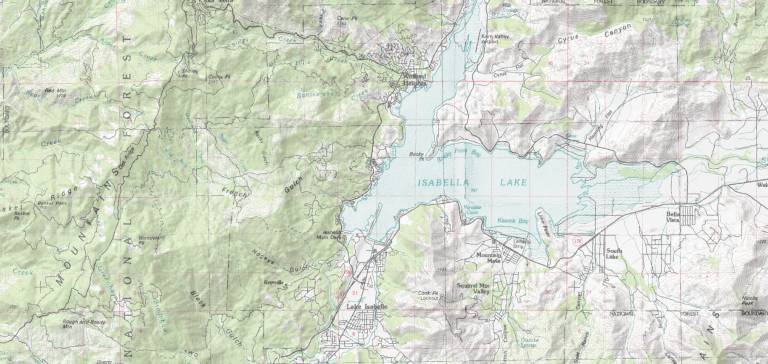
- DIGITAL RASTER GRAPHIC (DRG) are images of a U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) standard series topographic map georeferenced to the Universal Transverse Mercator projection.
- DIGITAL ORTHOPHOTOS QUADRANGLE (DOQ) is a geometrically-corrected orthophoto photograph at a scale of 1:40,000.
Let’s take a closer look at these USGS formats in a bit more detail.
What is a Digital Line Graph (DLG)?
Digital Line Graph (DLG) is a vector data format developed and distributed by the United States Geological Survey (USGS).
DLGs depict information about the geographic features of the terrain. Furthermore, it includes administrative, hydrography, transportation, man-made features, and more. As part of the National Mapping Program, the USGS prepared DLGs at medium to large scales.
Not to mention, all DLG data distributed by the USGS have a full structure of attribute codes. Further to this, topology has passed a high degree of quality control checks.
You can download Digital Line Graphs (DLG) from USGS Earth Explorer. Under the data sets tab, click the “Digital Line Graphs” option. From here, it’s a matter of choosing DLG 1:100K and DLG Large Scale and then adding them to your cart.
If you haven’t worked with this interface, here’s a quick tutorial on how to download USGS Earth Explorer data.
What is a Digital Orthophotos Quadrangle (DOQ)?
Digital Orthophotos Quadrangle (DOQ) is a geometrically-corrected photograph produced by the USGS. At about 1-meter pixel resolution, the spatial resolution is at 1:40,000.
In the 1980s, GIS was starting to develop. As a result, the USGS started producing DOQs as a point of reference. DOQs began production in 1991 by the USGS Western Mapping Center. But it was a short-lived effort, as DOQ creation shifted to the private section in 2000.
You can download Digital Orthophotos Quadrangle on the USGS Earth Explorer. Under the data sets tab, click the “Aerial Imagery” option and select the DOQ option. Here’s a quick tutorial on how to download USGS Earth Explorer data.
What is a Digital Raster Graphic?
Digital Raster Graphics (DRG) are digital version maps of USGS fine to medium scale topographic maps. DRGs are standard USGS topographic maps but they have map collar information.
Each DRG has a Universal Transverse Mercator projection using the North American Datum 1983. For example, features in these topographic maps include imagery (NAIP), roads (Interstate, route, ramp, and local roads), toponymy names, hydrography (rivers, lakes), elevation contours, and boundaries.
Here’s how to download Digital Raster Graphic GIS data.
The History of USGS Formats
TIGER has been releasing TIGER/Line files for over 20 years. In the 1980s, the US Census Bureau pioneered the creation of GBF/DIME coverage files. Each TIGER file used Dual Independent Map Encoding (DIME) for the encoding structure. Also, the file format developed for storing the DIME-encoded data was the Geographic Base Files (GBF).
During this same era, the USGS was developing its own GIS data called Digital Line Graphs (DLGs). DLGs are at a scale of 1:100,000 which includes transportation, hydrography, and United States boundaries.
The two federal agencies collaborated to build a national geospatial database merging their data. As part of this initiative, they included DLG files in GBF/DIME coverage files. This is when the US Census Bureau replaced the data format with Topologically Integrated Geographic Encoding and Referencing (TIGER) in 1990.