What’s the Difference Between CAD and GIS?

CAD vs GIS
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and GIS (Geographic Information Systems) are both types of software tools used to create digital models of the physical world.
Although they both use spatial data, they have substantial differences between them. This article will examine CAD vs GIS. Which one should you use?
Overview of CAD
CAD is a design technology used to create two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) as-built drawings, such as blueprints and models. Engineers, architects, and drafting technicians use CAD to develop drawings and plans for buildings, bridges, and other structures.
CAD software provides a wide range of features for creating precise and accurate drawings. Drafting technicians can also use it to create animations and simulations. But its main functionality is in architectural design, civil engineering, and mechanical engineering.
Recently, CAD systems have expanded into areas such as simulations, automation, and BIM. For instance, you can use CAD systems in conjunction with other computer software, such as computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software to produce and automate finished products.
Overview of GIS
GIS is a technology that captures, stores, analyzes, manages, and presents geographic data. GIS professionals use it for a variety of purposes, such as analyzing patterns and relationships in the environment, predicting potential outcomes, and making decisions.
Some common applications of GIS are in urban planning, land management, disaster response, and other applications where GIS data is needed. For example, GIS can find connections between data, such as linking environmental data with location data to create a map showing pollution levels in different areas
Although the main purpose is to create digital maps and visualizations about different aspects of the environment, GIS is heavy on data analysis. Since its invention, it has been evolving at the speed of light. The most recent Innovations include the areas of field data collection, cloud computing, data science, IoT, and machine learning.
Key Differences Between CAD and GIS
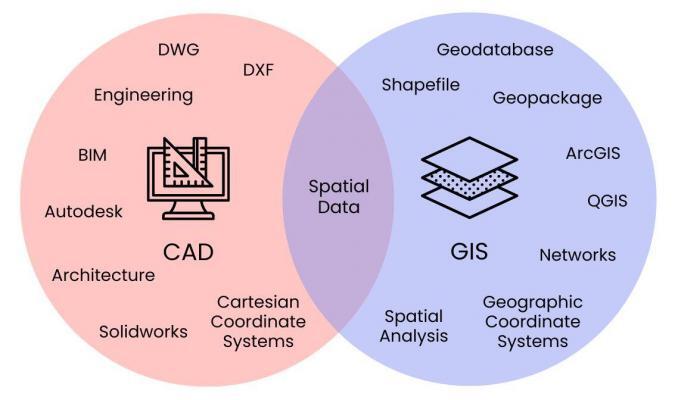
While both CAD and GIS are computer technologies used to create and manage spatial data, they are built to serve different purposes. This Venn diagram can help you understand some of their key differences:
1. Functionality
Design functionality is one of the main differences between CAD and GIS technology. While CAD is designed to create 2D and 3D designs, GIS is designed with physical locations in mind. CAD software allows users to create precise designs for drawings, schematics, graphs, and more.
GIS software, on the other hand, is about building maps and visualization for anything with geospatial characteristics. It’s often the case that GIS layers represent actual features on Earth. But CAD designs are conceptual.
2. Data Types and Structure
CAD software is designed to work with design data, such as architectural drawings and construction drawings. GIS, on the other hand, can be used to collect, analyze, and visualize any location on Earth.
GIS systems can store a wide variety of data types, including demographic data, health data, and much more. While CAD mostly uses DWG and DXF formats, GIS uses geodatabases, shapefile, geopackage, and other GIS formats. Don’t forget how easy it is to convert DWG to SHP (and vice versa).
3. Applications
Both CAD and GIS have a wide range of applications. But they typically have different areas of focus. CAD is mostly for designing physical objects, such as buildings, electrical circuits, and mechanical parts.
The main purpose of a GIS is to create visualizations and make connections between data, such as creating links between health data and location data. GIS applications include a wide variety of domains, including urban planning, disaster management, environmental management, resource management, and military operations.
4. Coordinate Systems
CAD and GIS both use coordinate systems to represent points, lines, and polygons in a 2D or 3D space. However, they differ in how the software uses coordinate systems. CAD often uses Cartesian coordinate systems, which is a coordinate system that represents a point on a plane by its x and y coordinates.
On the other hand, GIS uses geographic coordinate systems such as latitude and longitude to represent points on the Earth’s surface. Importing CAD data into GIS software often results in an unknown coordinate system.
5. Data Models
GIS data modeling offers a wide range of types compared to CAD. For vector data in GIS, you can work with network datasets, linear referencing systems, and topological networks. Additionally, raster data have complex data storage from mosaic datasets to multidimensional rasters. But CAD systems typically don’t support these types of data representations.
CAD Software
As mentioned, CAD software enables users to quickly and accurately create detailed 3D models and 2D drawings with specialized tools. The most popular software applications include AutoCAD and SolidWorks.
Autodesk – AutoCAD is one of the oldest and most popular CAD programs, offering advanced capabilities for industrial and mechanical design. Drafting technicians use it for everything from product design to architecture. In addition, it’s possible to use it in conjunction with other programs such as Revit for more complex projects.
Solidworks – Solidworks is another popular CAD program, designed for everything from basic drafting to complex 3D modeling. SolidWorks works well in fields such as mechanical engineering, product design, and manufacturing.
GIS Software
On the other hand, the most popular GIS software are Esri ArcGIS and QGIS.
Esri ArcGIS – Esri ArcGIS is the most popular GIS software in the world today. With Esri ArcGIS Pro software, businesses can better organize, analyze, and visualize large and complex datasets. ArcGIS includes a wide range of tools for map creation, geospatial analysis, data collection, and asset management. It is also one of the most innovative GIS companies today with its cloud platform, ArcGIS Online.
QGIS – QGIS is a popular open-source GIS software that offers many of the same features as ArcGIS. It is designed to be user-friendly for performing a variety of tasks, including georeferencing, data analysis, and cartography. But it’s important to note that QGIS has a wide range of plugins that you can use to extend its functionality.
Conclusion
The main difference between CAD and GIS is that the purpose of CAD is for designing 2D and 3D drawings, while GIS is for analyzing and visualizing spatial data.
There are also differences in how they handle coordinate systems and the complexity of data types in both software systems.
Although both technologies have different uses and serve different purposes, they can also be combined to create powerful tools for understanding the physical world.






I appreciate your input. The information is easy for understanding. Thank you