15 Best Remote Sensing Software

Remote Sensing Software
Whether you’re a professional geographer, a student of Earth science, or just a curious hobbyist, there is a great variety of remote sensing software available to help you get the job done.
From classifying detailed aerial images to creating sophisticated 3D models, these 10 remote sensing software packages are the best of the best. Let’s dive right in.
1. ERDAS Imagine
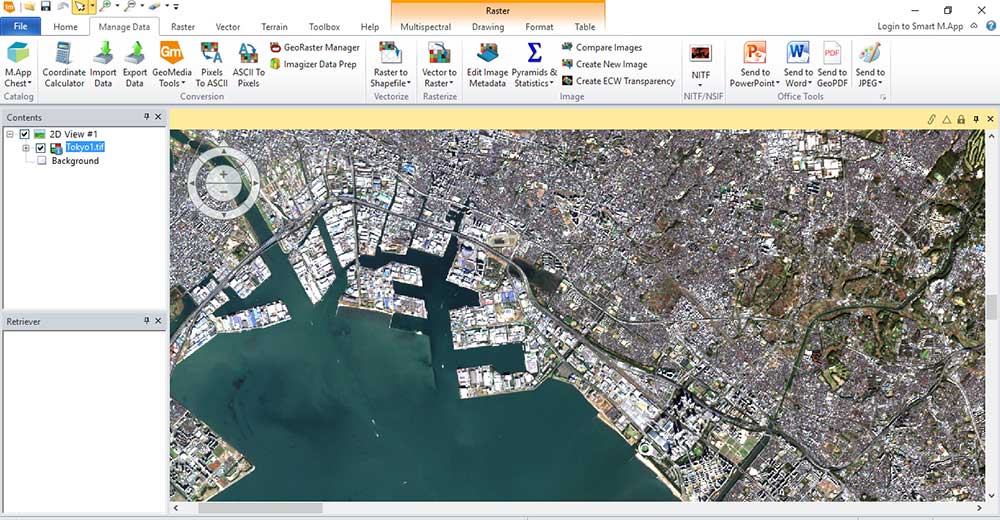
ERDAS Imagine is ranked as our #1 remote sensing and image analysis software suite. Developed by Hexagon Geospatial, it can handle virtually any type of geospatial data. This includes satellite imagery, aerial photography, LiDAR point clouds, digital elevation models, and other GIS data.
ERDAS Imagine is a powerhouse for remote sensing. It lets users do advanced image processing, 3D visualization, and feature extraction. Plus, it provides an intuitive ribbon-based interface to find the right tool for the job.
Some of its standout features include its Spatial Model Editor, point cloud processing, and photogrammetry tools. This is why it’s always one of the top picks for remote sensing software in industries such as agriculture, forestry, mining, engineering, urban planning, and defense.
READ MORE: ERDAS Imagine – Earth Resources Data Analysis System
2. ENVI
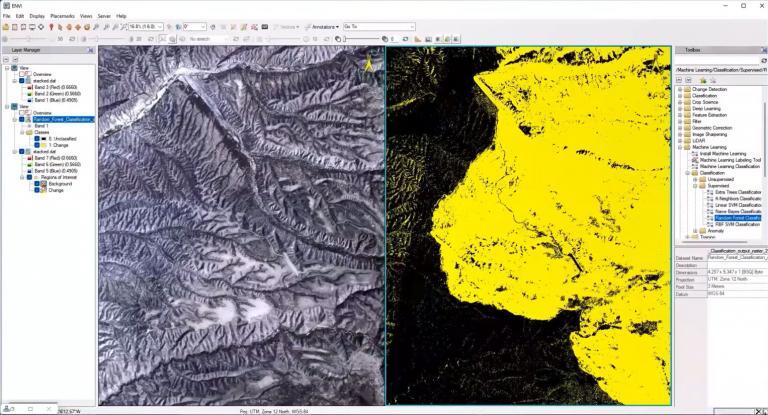
ENVI is an advanced remote sensing software platform from NV5 Geospatial. With ENVI, users can quickly extract information from satellite, airborne, and other types of imagery by leveraging the latest in image processing technology.
ENVI’s comprehensive set of features and capabilities allows users to perform a variety of image processing tasks. For instance, this included image enhancement, feature extraction, image segmentation, statistical analysis, change detection, and visualization.
It provides support for a wide range of data formats, including those from commercial sources such as Maxar, Airbus, and Planet. ENVI also offers powerful automation capabilities through ENVI modeler to automate repetitive tasks.
3. PCI Geomatica (Catalyst)
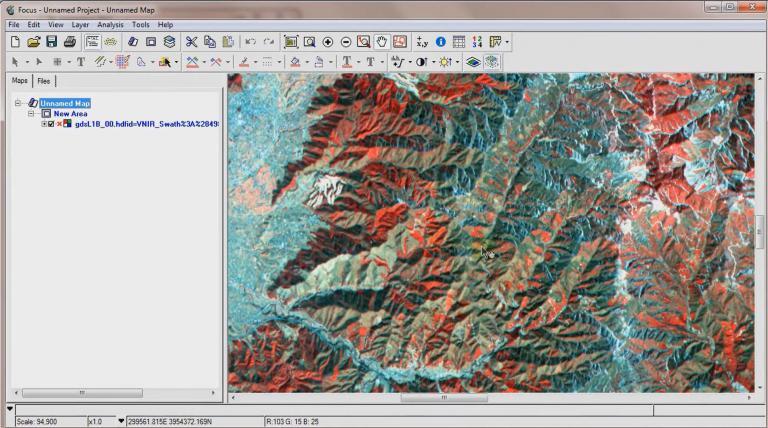
PCI Geomatica is an advanced remote sensing software suite used by scientists, researchers, and GIS professionals around the world. Developed by Canadian company PCI Geomatics, users can access and analyze satellite imagery, aerial photography, and other types of remotely sensed data.
Since 1982, PCI Geomatica has provided a solid foundation for processing data from a variety of sources. This includes aerial photos, satellite imagery, digital elevation models, and SAR and InSAR data. Although the interface is a bit dated, you still get the core tools like mosaicking, photogrammetry, and terrain analysis.
It also has plug-and-play feature extraction capabilities that make it easy to detect features in digital images. Algorithms include OBIA, supervised and unsupervised classification. This means that users can extract information like roads, buildings, and vegetation from aerial or satellite imagery.
4. ArcGIS Pro
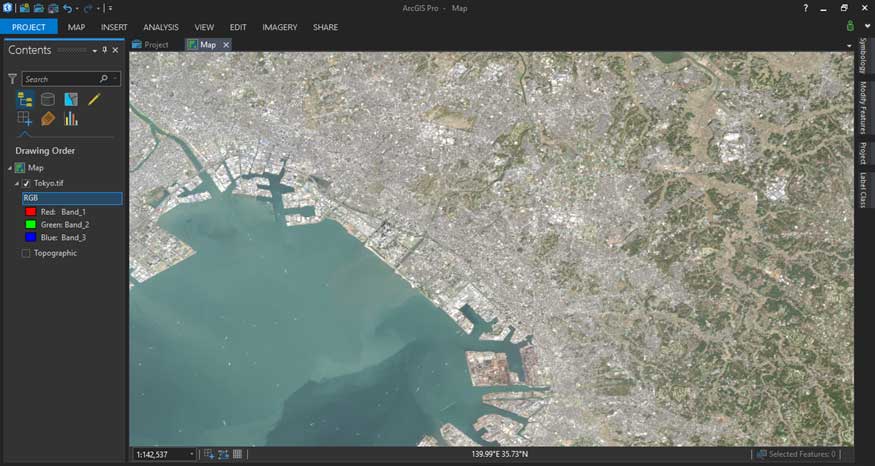
The bulk of remote sensing tools in ArcGIS Pro can be found in the Image Analysis extension. This extension provides access to a set of tools for analyzing imagery and performing advanced image analysis tasks.
For instance, it enables users to create and modify raster datasets, visualize and explore imagery. You can also execute more sophisticated analyses including terrain analysis, image classification, and spectral analysis.
With the Image Analysis extension, you can quickly process large amounts of imagery and extract valuable information from it. You can also use its imagery workflows to perform a set of tasks such as time-series analysis and change detection with deep learning.
5. QGIS 3
QGIS 3 is loaded with remote sensing tools by default like its raster analysis, terrain analysis, and interpretation toolboxes. But QGIS 3 isn’t limited to just its own toolboxes, you can leverage a wealth of capabilities using toolboxes from SAGA GIS, GDAL, and GRASS GIS.
If you’ve ever used QGIS before, you’ll know that you can extend its capabilities by using plugins. One of its most popular remote sensing plugins is the free open source Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin (SCP) plugin.
The SCP plugin provides many features and functions such as allowing users to quickly and easily download and classify satellite imagery. There are also algorithms for pre-processing, post-classification improvement, accuracy assessment, and much more.
READ MORE: 35 Differences Between ArcGIS Pro and QGIS 3
6. Trimble eCognition
Trimble eCognition is a specialist in feature extraction through the means of object-based image analysis (OBIA). If you’ve ever used eCognition, you’ll know it uses pattern-recognition algorithms to divide imagery into meaningful objects (not just pixels).
After executing a multi-resolution segmentation algorithm, each object has statistics associated with them. By using spectral and spatial characteristics, you can create the most advanced land cover classification today. Further to this, you can build rulesets to automate land cover creation and apply them to various types of imagery.
Trimble eCognition accepts a variety of inputs such as LiDAR point clouds, aerial, satellite, and UAV imagery. Although it highly succeeds in land cover development, it’s not a complete remote sensing suite. Because it lacks common tools such as georeferencing, 3D visualization, or SAR capabilities, it doesn’t get a homerun rating from us.
READ MORE: Nearest Neighbor Classification Guide in eCognition
7. Birdi

This one’s slightly different from the others. It’s not your typical remote sensing software that you download on your machine. Instead, you use Birdi as a SaaS for creating and uploading drone missions.
The best use case I find it’s for is using your drone imagery to assess assets. This includes everything from geotagged images to 360 cameras. From there, you markup polygons, add recommended actions and generate reports.
It’s a platform that you can combine all your remote sensing data. You can share maps with clients and set permissions to edit or view. It’s also good for measuring areas, lengths and volumes.
8. SAGA GIS
Admittedly, SAGA GIS is a bit rough around the edges. It’s an older remote sensing software so it’s definitely not as polished as the others on this list. But with that said, there’s still a lot you can salvage from it.
SAGA GIS has a wide range of features that allow users to perform basic data processing and analysis tasks related to remote sensing. For example, you can use it to mosaic, clip, and split imagery, as well as transform image projections. It also offers tools for analyzing vegetation indices, calculating surface area, and extracting features from digital elevation models.
For open source remote sensing software, you get a ton of tools. Honestly, some tools we’ve never heard of. But the more you explore them, you’ll learn that some may not be reliable and 100% functional. But it’s still worth the time and effort to check it out for its rare remote sensing tools. And don’t forget that you can leverage the SAGA GIS toolbox in QGIS 3 too.
9. PolSARPro
As the name suggests, PolSARpro (Polarimetric SAR Data Processing and Education Toolbox) is a specialist in radar imagery. This includes the following types of satellite sensors:
- ALOS-1
- COSMO-SkyMed
- RADARSAT-2
- TerraSAR-X and TanDEM-X
PolSARPro is an advanced software package designed for the analysis and visualization of polarimetric synthetic aperture radar (PolSAR) data. It is capable of providing detailed information about surface features, soil moisture, and other characteristics of the Earth’s surface from radar-based measurements.
10. GRASS GIS
GRASS GIS is a long-standing open source software in the world of GIS. Not without its quirks, GRASS GIS is still well suited for remote sensing applications.
GRASS GIS also offers a suite of advanced tools for working with LiDAR data, such as point cloud classification, filtering, and interpolation. Similar to SAGA GIS, you can leverage it in QGIS 3, or you can use it as a standalone application.
Overall, the software has an array of features specifically designed for remote sensing analysis, including image classification, enhancement, and registration. Additionally, GRASS GIS provides an impressive suite of tools for data visualization, allowing users to quickly create maps and 3D analysis with their data.
READ MORE: GRASS GIS – Geographic Resources Analysis Support System
11. ILWIS
ILWIS (Integrated Land and Water Information System) is a geographic information system (GIS) designed to store, manage and analyze spatial data.
It is developed by ITC, in the Netherlands, and is used for various applications including land use planning, land cover analysis, soil mapping, water management, environmental monitoring, and many more.
READ MORE: ILWIS – Integrated Land and Water Information Management
12. Orfeo Toolbox
ORFEO Toolbox (OTB) is an open-source library of image processing algorithms developed by the French Space Agency (CNES). One of the nice things about this framework is how it is written in C++ and runs on Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux. OTB provides a wide variety of ready-to-use algorithms for remote sensing and digital image processing.
13. Global Mapper
Global Mapper is capable of displaying both topographic and satellite imagery, allowing users to accurately visualize and analyze the terrain in any location. It also offers powerful yet easy-to-use tools such as digitizing, line of sight calculations, and volume calculations that are useful for many different types of analysis.
Global Mapper allows users to visualize, analyze, and manipulate spatial data from a variety of sources, including aerial imagery, LiDAR point clouds, digital elevation models, and vector databases.
14. Feature Manipulation Engine
The Feature Manipulation Engine (FME) is a king at interoperability and automation with lots of raster transformers you can incorporate into your workbenches. FME has the capability to process data from various remote sensing sources such as aerial photography, LiDAR, and multispectral imagery, and more.
But some of its most exciting developments are in the fields of computer vision and deep learning. FME also allows users to automate their remote sensing workflows, making it easier and faster to analyze data.
READ MORE: FME Software – Feature Manipulation Engine (Review)
15. Whitebox GAT
We’ve always had a special place in our hearts for Whitebox GAT (Geospatial Analysis Toolbox) and still do. If you’ve never used it before, it’s an open source geospatial analysis tool for a variety of uses. It is available as a standalone application as well as a library for use in other software.
In a nutshell, Whitebox GAT contains an advanced toolbox for working with remote sensing data. Its extensive library of functions makes it a great choice for those who need to perform a variety of tasks with their data.
Although it specializes in hydrological tools, Whitebox GAT provides a range of features that make it suitable for remote sensing applications. For instance, this includes the ability to work with both raster and vector data, support for various spatial interpolation methods, and a comprehensive suite of terrain analysis tools. Not to mention, Whitebox GAT has excellent LiDAR capabilities.
READ MORE: WhiteBox GAT – Geospatial Analysis Toolbox (Review)
Conclusion
Remote sensing provides a powerful way to turn data into actionable intelligence. If you are looking for a dedicated remote sensing software suite, we recommend working with ERDAS Imagine, ENVI, or PCI Geomatica.
If you’re looking for strong GIS capabilities, ArcGIS Pro and QGIS 3 provide an entry point for people who also want a high-end mapping platform. While Trimble eCognition is strictly for OBIA land cover classification, PolSARPro specializes in radar-based imagery.
If you’re flying drones, then use Birdi. Finally, if you’re looking for open source remote sensing software, then QGIS 3, Whitebox GAT, GRASS GIS, and SAGA GIS are your best bets.
Changelog
- July 29, 2025 – Removed gvSIG. Added Birdi. Whitebox GAT moved down to #15, as it no longer provides a user interface.





Which software I can use to process worldview legion imagery
You should be able to work with it using QGIS, as an open source option. ArcGIS Pro and most other remote sensing software can handle it.
Terrset should definitely be closer to the top of the list. Its land use modelling programs are second to none.