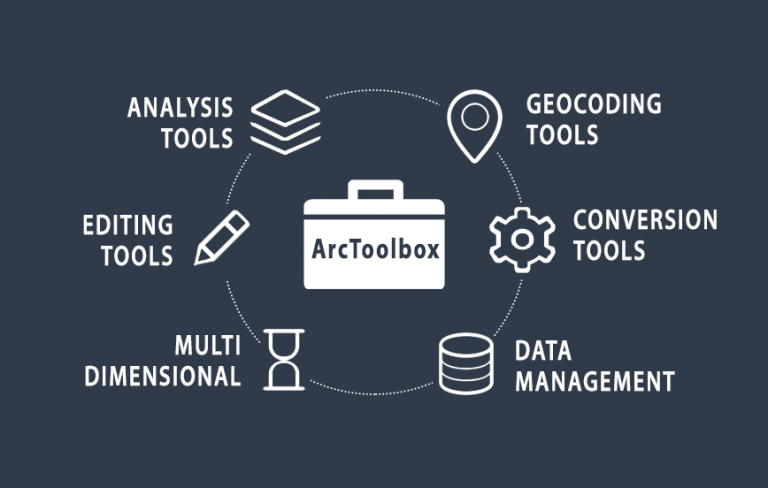
What is ArcToolbox?
DEFINITION:
ArcToolbox is a component of ArcGIS that provides a collection of tools for performing various spatial analysis, data management, and geoprocessing tasks.
What is ArcToolbox?
ArcToolbox is a collection of geoprocessing tools for analyzing, editing, and converting data.
ArcGIS and ArcGIS Pro have 20 or so common toolboxes for ArcToolbox. Each toolbox has a unique set of specialized tools for spatial analysis.
Some toolboxes are available as part of the default ArcGIS installation. But others are available through ArcGIS extensions and add-ons.
This article is dedicated to reviewing all the toolsets that are a part of ArcToolbox.
ArcToolbox organizes each toolbox in the following way:
- TOOLBOX: Main container for toolsets and tools
- TOOLSET: Secondary container with tools
- TOOL: A single geoprocessing operation.
3D Analyst Tools
3D Analyst Tools provides tools to work in 3D. For example, you can work with CityEngine, LAS, and multipatch features. Here are some examples of what you can do with 3D analysis tools:
- Analyze 3D features using tools like buffers, intersect, and union.
- Recognize visibility like line-of-sight, viewsheds, and skylines.
- Measure 3D surfaces, volumes, and slopes
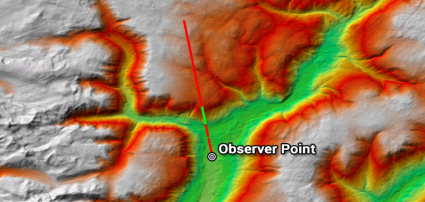
As part of the 3D analyst extension, you can use the line-of-sight tool. Then, if you use a digital elevation model, you can determine obstructed (red) and unobstructed (green) sections from a line.
Analysis Tools
The analysis tools perform the most fundamental spatial analysis operations. For example, it has your basic extract, map overlay, and proximity tools. But it also solves basic statistics like finding the mean, counts, and standard deviation.
- Perform overlay operations like intersect, union, and spatial join.
- Find proximity using the buffer tool and near tables.
- Extract features by selecting, clipping, and splitting features.
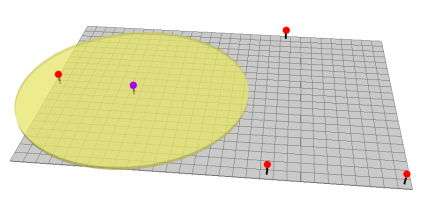
The buffer is an example of a tool in the analysis tools. When you set a value, it generates a polygon around features at a set distance.
Cartography Tools
Cartography tools refine data for the production of maps. For example, you can create graticules and grids. You can also generalize features for display at different map scales.
- Generate graticules as references for maps.
- Generalize features by smoothing, simplifying, and thinning.
- Produce grid indexes and strip maps for data driven pages.
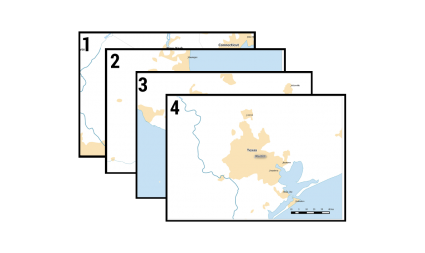
In this example, you can generate strip map grids along a line. Then later, you can create a mapbook using these grids as the reference index.
Conversion Tools
Conversion tools alter data types between different GIS file formats. For example, you can convert tables, vectors, and raster data.
You can also work with web, 3D, and CAD files too.
Data Interoperability Tools

Data interoperability tools convert file types using Safe Software’s Feature Manipulation Engine (FME) technology.
Because FME supports 450+ file formats, it helps you connect with a wide range of data. This means you can access data that ArcGIS does not natively support.
- Quick export/import using FME data interoperability to extract, load and transform data.
Data Management Tools
Data management tools help develop, manage and maintain data structures and types of files.
Also, it includes tools to detect changes, administer geodatabase, and project data. Data management tools include support for the following file types and more:
Editing Tools
Editing tools provide a way to bulk edit a set of features. So, instead of just editing a single feature as you would do with the Editor Toolbar. You can apply edits to multiple features using tools. If you don’t want to edit all features, you can make a selection from your features.
- Generalize, densify, extend, snap and erase a set of features.
- Conflate two datasets by aligning features at boundary lines.
For example, the “extend” tool ensures that all lines stretch and snap to a boundary. By running this tool, you ensure that all lines extend given a tolerance value.
Geocoding Tools
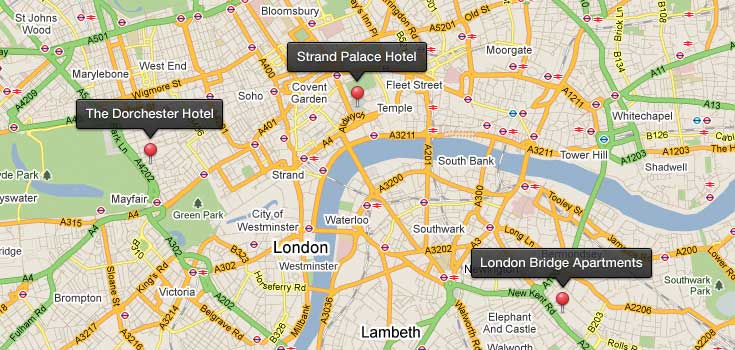
Geocoding tools assign a location with a descriptive location’s address. For example, it includes a postal address such as street name, zip code, or census tract.
- Geocoding gives longitude and latitude values to street addresses.
- Reverse geocoding takes locations from a map and identifies their postal addresses.
In this example, the user gives a list of addresses. Next, the geocoding service finds matches by adding locations on the map.
Geostatistical Analyst Tools
The geostatistical analyst tools are similar to the spatial analyst tools. But you can access highly specialized tools for geostatistics. Using geostatistics, you can better model spatial patterns and recognize uncertainty.
- Execute kriging interpolation and find the amount of standard error at each location.
- Process Empirical Bayesian Kriging (EBK) by repeating various simulations.
Using geostatistical analyst tools, you can perform kriging. Not only does it create a prediction surface, but it also generates a standard error so you know the level of uncertainty.
Linear Referencing Tools
Linear Referencing Tools stores relative positions along existing line features. For example, roads, rivers, and sewer networks are lines and can make use of linear referencing. Instead of a regular line, linear referencing (routes) has positions and measurements along it.
- Create calibrate and locate features along routes
Linear referencing adds m-values to routes with events. Events are linear or continuous point features along a route. For each vertex, m-values store the relative distance along the route.
Multidimensional Tools
Multitemporal data has a time component attached to it. For example, weather data uses temporal GIS data formats because of how important time is related to weather. Other examples of temporal data are demographic trends, land use patterns, and lightning strikes.
- Multidimensional Tools are designed to make and select rasters in NetCDF formats.
This example is meant to show land use patterns that change over time in a NetCDF format.
Network Analyst Tools
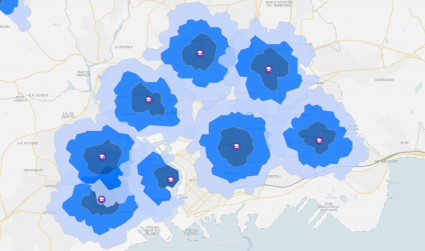
The Network Analyst tools support the maintenance and analysis of network datasets. Typically, this toolset works primarily with road networks.
- Build network data sets with nodes, direction, and connectivity.
- Find the shortest path, optimal service locations and work with other types of network analysis.
Using the network analyst tools, you can leverage the connectivity of nodes with direction. Service areas are areas that can be reached within an allotted amount of time. In this case, this is where fire stations can service the fastest and slowest.
Parcel Fabric Tools
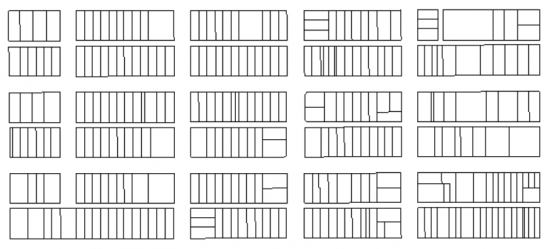
Parcel fabric tools are a set of operations for the creation and maintenance of quarter sections, lots, and parcels.
All parcels are contiguous, connected and stored in Coordinate Geometry (COGO). That is, each coordinate and dimension has been recorded from a surveyed plan.
- Creates, appends, and copies a parcel fabric layer from an input parcel fabric.
This is an example of a parcel fabric. Each parcel is bounded by one another with Coordinate Geometry (COGO).
Schematics Tools
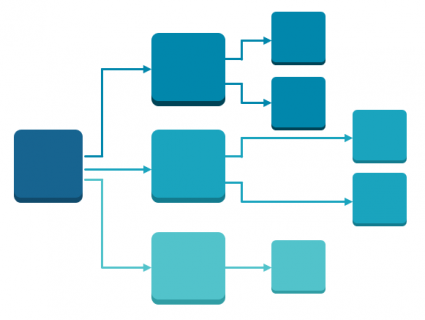
The schematics extension automatically generates a simplified diagram of your network. Instead of viewing real-world locations and coordinates, you can create a representation. This way, it’s easy to read and understand its basic structure.
- Create, convert, and update diagrams using the schematic builder.
Schematics are simplified diagram representations good for utilities, traffic, and network diagrams. Schematics tools create, update, and export diagrams or create schematic folders.
Server Tools
Server Tools manages ArcGIS Server map and globe caches for faster display.
- Create, manage, and upgrade caches for a map server
- Publish MXD to web maps through Portal
Space Time Pattern Mining Tools
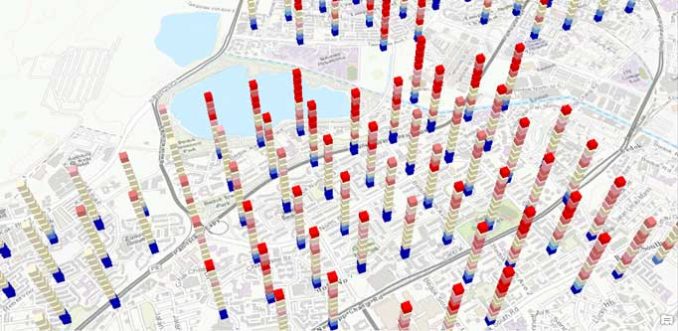
Space time cubes are slices of time stacked up in a three-dimensional space. Older time cubes are on the bottom.
Then, new slices of time are on top. So, this makes it ideal to show how values change in geographic space (4D).
- Create space time cubes, emerging hot spots, and local outliers
Spatial Analysis Tools
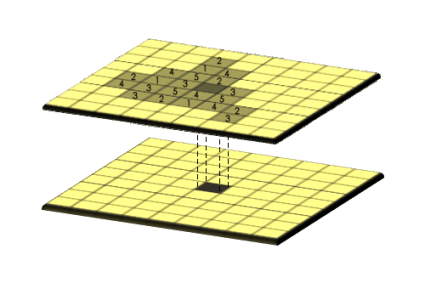
The spatial analyst extension is for specialized raster analysis. By analyzing raster data cell-by-cell, you can perform map algebra and zonal statistics. For example, this extension allows you to:
- Generate least-cost distance corridors and basic interpolation.
- Create land cover by image classification techniques.
- Perform groundwater, hydrology, and solar radiation analysis.
Spatial Statistics Tools
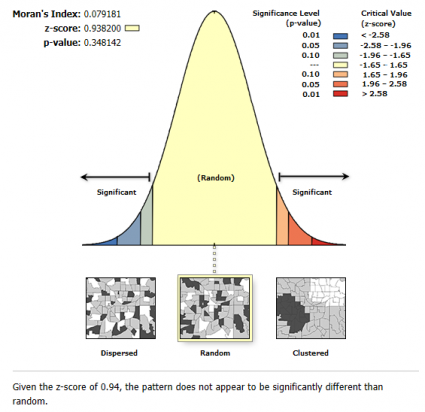
Spatial statistics tools are designed for statistical analysis. For example, it examines spatial distributions, patterns, processes, and relationships.
- Analyze geographic patterns with spatial autocorrelation and Moran I.
- Map out clusters and optimized hot spots.
- Measure spatial distribution such as geographic mean centers.
- Model spatial patterns with geographically weighted regression.
Tracking Analysis Tools
The tracking analyst extension is for moving objects with the dimension of time. By integrating with GPS, it tracks the movement of anything historic or in real-time.
Also, because you have time, you can chart it out through time series animation and work within the Internet of Things (IoT) in GIS.
- Make tracking layer using temporal layer.
Summary: What is ArcToolbox?
We’ve reviewed the main toolsets for ArcToolbox. Each one provides a set of unique tools in ArcGIS Desktop and ArcGIS Pro.
But there are more that we didn’t have time to mention.
For example, there are toolboxes for aviation, business analysts, and more.
Learn more about the extensions for ArcMap.











Je souhaiterai avoir une bourse pour maitriser ArcGis